The cribriform pattern identifies a subset of acinar predominant tumors with poor prognosis in patients with stage I lung adenocarcinoma: a conceptual proposal to classify cribriform predominant tumors as a distinct histologic subtype
- PMID: 24186133
- PMCID: PMC4374572
- DOI: 10.1038/modpathol.2013.188
The cribriform pattern identifies a subset of acinar predominant tumors with poor prognosis in patients with stage I lung adenocarcinoma: a conceptual proposal to classify cribriform predominant tumors as a distinct histologic subtype
Abstract
The 2011 International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC)/American Thoracic Society (ATS)/European Respiratory Society (ERS) lung adenocarcinoma classification emphasizes the prognostic significance of histologic subtypes. However, one limitation of this classification is that the highest percentage of patients (∼40%) is classified as acinar predominant tumors, and these patients display a spectrum of favorable and unfavorable clinical behaviors. We investigated whether the cribriform pattern can further stratify prognosis by histologic subtype. Tumor slides from 1038 patients with stage I lung adenocarcinoma (1995-2009) were reviewed. Tumors were classified according to the IASLC/ATS/ERS classification. The percentage of cribriform pattern was recorded, and the cribriform predominant subtype was considered as a subtype for analysis. The log-rank test was used to analyze the association between histologic variables and recurrence-free probability. The 5-year recurrence-free probability for patients with cribriform predominant tumors (n=46) was 70%. The recurrence-free probability for patients with cribriform predominant tumors was significantly lower than that for patients with acinar (5-year recurrence-free probability, 87%; P=0.002) or papillary predominant tumors (83%; P=0.020) but was comparable to that for patients with micropapillary (P=0.34) or solid predominant tumors (P=0.56). The recurrence-free probability for patients with ≥10% cribriform pattern tumors (n=214) was significantly lower (5-year recurrence-free probability, 73%) than that for patients with <10% cribriform pattern tumors (n=824; 84%; P<0.001). In multivariate analysis, patients with acinar predominant tumors with ≥10% cribriform pattern remained at significantly increased risk of recurrence compared with those with <10% cribriform pattern (P=0.042). Cribriform predominant tumors should be considered a distinct subtype with a high risk of recurrence, and presence (≥10%) of the cribriform pattern is an independent predictor of recurrence, identifying a poor prognostic subset of acinar predominant tumors. Our findings highlight the important prognostic value of comprehensive histologic subtyping and recording the percentage of each histologic pattern, according to the IASLC/ATS/ERS classification with the addition of the cribriform subtype.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors affirm no actual or potential conflicts of interest, including any financial, personal, or other relationships with other people or organizations.
Figures

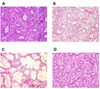
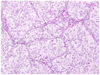

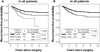

References
-
- Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2011. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:212–236. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Devesa SS, Bray F, Vizcaino AP, Parkin DM. International lung cancer trends by histologic type: male:female differences diminishing and adenocarcinoma rates rising. Int J Cancer. 2005;117:294–299. - PubMed
-
- Motoi N, Szoke J, Riely GJ, et al. Lung adenocarcinoma: modification of the 2004 WHO mixed subtype to include the major histologic subtype suggests correlations between papillary and micropapillary adenocarcinoma subtypes, EGFR mutations and gene expression analysis. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008;32:810–827. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

