Emphysema and mechanical stress-induced lung remodeling
- PMID: 24186935
- PMCID: PMC3858211
- DOI: 10.1152/physiol.00041.2013
Emphysema and mechanical stress-induced lung remodeling
Abstract
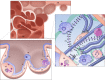
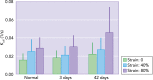
Transpulmonary pressure and the mechanical stresses of breathing modulate many essential cell functions in the lung via mechanotransduction. We review how mechanical factors could influence the pathogenesis of emphysema. Although the progression of emphysema has been linked to mechanical rupture, little is known about how these stresses alter lung remodeling. We present possible new directions and an integrated multiscale view that may prove useful in finding solutions for this disease.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the author(s).
Figures



Comment in
-
Physiology's impact: Applying mathematics and advanced technologies.Physiology (Bethesda). 2013 Nov;28(6):363-5. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00051.2013. Physiology (Bethesda). 2013. PMID: 24186929 No abstract available.
-
Regenerative medicine: why does it matter?Physiology (Bethesda). 2013 Nov;28(6):366-7. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00054.2013. Physiology (Bethesda). 2013. PMID: 24186930 No abstract available.
-
Physiology in perspective: cell migration and the regenerative process.Physiology (Bethesda). 2013 Nov;28(6):368-9. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00052.2013. Physiology (Bethesda). 2013. PMID: 24186931 No abstract available.
References
-
- Alencar AM, Arold SP, Buldyrev SV, Majumdar A, Stamenovic D, Stanley HE, Suki B. Physiology: dynamic instabilities in the inflating lung. Nature 417: 809–811, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Arold SP, Suki B, Alencar AM, Lutchen KR, Ingenito EP. Variable ventilation induces endogenous surfactant release in normal guinea pigs. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 285: L370–L375, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Baglole CJ, Bushinsky SM, Garcia TM, Kode A, Rahman I, Sime PJ, Phipps RP. Differential induction of apoptosis by cigarette smoke extract in primary human lung fibroblast strains: implications for emphysema. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 291: L19–L29, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Barnes PJ. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med 343: 269–280, 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

