Thymic regulatory T cell development: role of signalling pathways and transcription factors
- PMID: 24187564
- PMCID: PMC3803129
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/617595
Thymic regulatory T cell development: role of signalling pathways and transcription factors
Abstract
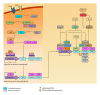
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) are a subset of CD4 T cells that are key mediators of immune tolerance. Most Tregs develop in the thymus. In this review we summarise recent findings on the role of diverse signalling pathways and downstream transcription factors in thymic Treg development.
Figures

References
-
- Klein L, Hinterberger M, Wirnsberger G, Kyewski B. Antigen presentation in the thymus for positive selection and central tolerance induction. Nature Reviews Immunology. 2009;9(12):833–844. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Asano M, Itoh M, Toda M. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor α-chains (CD25): breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune diseases. Journal of Immunology. 1995;155(3):1151–1164. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi S, Yamaguchi T, Nomura T, Ono M. Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell. 2008;133(5):775–787. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

