Rebaudioside A and Rebaudioside D bitterness do not covary with Acesulfame K bitterness or polymorphisms in TAS2R9 and TAS2R31
- PMID: 24187601
- PMCID: PMC3811954
- DOI: 10.1007/s12078-013-9149-9
Rebaudioside A and Rebaudioside D bitterness do not covary with Acesulfame K bitterness or polymorphisms in TAS2R9 and TAS2R31
Abstract
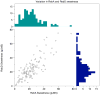
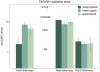
In order to reduce calories in foods and beverages, the food industry routinely uses non-nutritive sweeteners. Unfortunately, many are synthetically derived, and many consumers have a strong preference for natural sweeteners, irrespective of the safety data on synthetic non-nutritive sweeteners. Additionally, many non-nutritive sweeteners elicit aversive side tastes such as bitter and metallic in addition to sweetness. Bitterness thresholds of acesulfame-K (AceK) and saccharin are known to vary across bitter taste receptors polymorphisms in TAS2R31. RebA has shown to activate hTAS2R4 and hTAS2R14 in vitro. Here we examined bitterness and sweetness perception of natural and synthetic non-nutritive sweeteners. In a follow-up to a previous gene-association study, participants (n=122) who had been genotyped previously rated sweet, bitter and metallic sensations from rebaudioside A (RebA), rebaudioside D (RebD), aspartame, sucrose and gentiobiose in duplicate in a single session. For comparison, we also present sweet and bitter ratings of AceK collected in the original experiment for the same participants. At similar sweetness levels, aspartame elicited less bitterness than RebD, which was significantly less bitter than RebA. The bitterness of RebA and RebD showed wide variability across individuals, and bitterness ratings for these compounds were correlated. However, RebA and RebD bitterness did not covary with AceK bitterness. Likewise, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) shown previously to explain variation in the suprathreshold bitterness of AceK (rs3741845 in TAS2R9 and rs10772423 in TAS2R31) did not explain variation in RebA and RebD bitterness. Because RebA activates hT2R4 and hT2R14, a SNP in TAS2R4 previously associated with variation in bitterness perception was included here; there are no known functional SNPs for TAS2R14. In present data, a putatively functional SNP (rs2234001) in TAS2R4 did not explain variation in RebA or RebD bitterness. Collectively, these data indicate the bitterness of RebA and RebD cannot be predicted by AceK bitterness, reinforcing our view that bitterness is not a simple monolithic trait that is high or low in an individual. This also implies consumers who reject AceK may not find RebA and RebD aversive, and vice versa. Finally, RebD may be a superior natural non-nutritive sweetener to RebA, as it elicits significantly less bitterness at similar levels of sweetness.
Keywords: Project GIANT-CS; bitterness; genetics; non-nutritive sweetener; rebaudioside A; rebaudioside D; taste phenotype.
Conflict of interest statement
The corresponding author has been paid for developing and delivering educational presentations on taste perception and taste biology for the food industry; his laboratory also conducts routine consumer acceptability tests for the food industry to facilitate practical training for students. None of these companies have provided any direct or indirect support for the work described here. The RebD was kindly donated by Dr. Jeannine Delwiche at PepsiCo; PepsiCo did not provide any funding for this project, and was not involved in the design of the experiment or the decision to publish this work. The authors declare no other relationships or activities that may have influenced the work described here.
Figures




References
-
- Alarcon S, Tharp A, Tharp C, Breslin PA. The effect of polymorphisms in 4 hTAS2R genes on PROP bitterness perception. Chem Senses. 2008;33(8):S43.
-
- Bartoshuk LM, Duffy VB, Miller IJ. PTC/PROP tasting: Anatomy, psychophysics, and sex effects. Physiol Behav. 1994;56(6):1165–1171. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
