Telocytes in human oesophagus
- PMID: 24188731
- PMCID: PMC4117563
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.12149
Telocytes in human oesophagus
Abstract
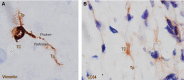
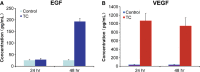
Telocytes (TCs), a new type of interstitial cells, were identified in many different organs and tissues of mammalians and humans. In this study, we show the presence, in human oesophagus, of cells having the typical features of TCs in lamina propria of the mucosa, as well as in muscular layers. We used transmission electron microscopy (TEM), immunohistochemistry (IHC) and primary cell culture. Human oesophageal TCs present a small cell body with 2-3 very long Telopodes (Tps). Tps consist of an alternation of thin segments (podomers) and thick segments (podoms) and have a labyrinthine spatial arrangement. Tps establish close contacts ('stromal synapses') with other neighbouring cells (e.g. lymphocytes, macrophages). The ELISA testing of the supernatant of primary culture of TCs indicated that the concentrations of VEGF and EGF increased progressively. In conclusion, our study shows the existence of typical TCs at the level of oesophagus (mucosa, submucosa and muscular layer) and suggests their possible role in tissue repair.
Keywords: EGF; VEGF; human oesophagus; stromal synapses; telocytes; telopodes; tissue repair.
© 2013 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures

References
-
- Suciu L, Popescu LM, Gherghiceanu M, et al. Telocytes in human term placenta: morphology and phenotype. Cells Tissues Organs. 2010;192:325–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

