Development and accuracy of quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction assays for detection and quantification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) heat labile and heat stable toxin genes in travelers' diarrhea samples
- PMID: 24189361
- PMCID: PMC3886408
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.13-0383
Development and accuracy of quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction assays for detection and quantification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) heat labile and heat stable toxin genes in travelers' diarrhea samples
Abstract
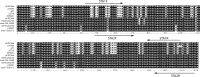
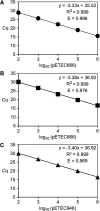
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC), the leading bacterial pathogen of travelers' diarrhea, is routinely detected by an established DNA hybridization protocol that is neither sensitive nor quantitative. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) assays that detect the ETEC toxin genes eltA, sta1, and sta2 in clinical stool samples were developed and tested using donor stool inoculated with known quantities of ETEC bacteria. The sensitivity of the qPCR assays is 89%, compared with 22% for the DNA hybridization assay, and the limits of detection are 10,000-fold lower than the DNA hybridization assays performed in parallel. Ninety-three clinical stool samples, previously characterized by DNA hybridization, were tested using the new ETEC qPCR assays. Discordant toxin profiles were observed for 22 samples, notably, four samples originally typed as ETEC negative were ETEC positive. The qPCR assays are unique in their sensitivity and ability to quantify the three toxin genes in clinical stool samples.
Figures



References
-
- Hill DR, Beeching NJ. Travelers' diarrhea. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2010;23:481–487. - PubMed
-
- Gyles C, So M, Falkow S. The enterotoxin plasmids of Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1974;130:40–49. - PubMed
-
- Crossman LC, Chaudhuri RR, Beatson SA, Wells TJ, Desvaux M, Cunningham AF, Petty NK, Mahon V, Brinkley C, Hobman JL, Savarino SJ, Turner SM, Pallen MJ, Penn CW, Parkhill J, Turner AK, Johnson TJ, Thomson NR, Smith SG, Henderson IR. A commensal gone bad: complete genome sequence of the prototypical enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strain H10407. J Bacteriol. 2010;192:5822–5831. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

