The KRAB zinc finger protein RSL1 modulates sex-biased gene expression in liver and adipose tissue to maintain metabolic homeostasis
- PMID: 24190968
- PMCID: PMC3911292
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00875-13
The KRAB zinc finger protein RSL1 modulates sex-biased gene expression in liver and adipose tissue to maintain metabolic homeostasis
Abstract
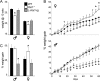
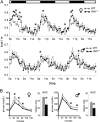
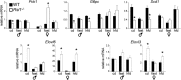
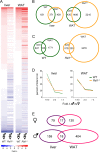
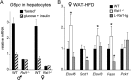
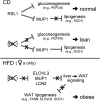
Krüppel-associated box zinc finger proteins (KRAB-ZFPs) are a huge family of vertebrate-specific repressors that modify gene expression in an epigenetic manner. Despite a well-defined repression mechanism, few biological roles or gene targets of KRAB-ZFP are known. Regulator of sex-limitation 1 (RSL1) is a mouse KRAB-ZFP that enforces male-predominant expression in the liver, affecting body mass and pubertal timing. Here we show that female but not male Rsl1(-/-) mice gain more weight than wild-type mice on a high-fat diet (HFD) and that key liver and white adipose tissue (WAT) metabolic genes are altered in both Rsl1(-/-) sexes in response to dietary stress. Expression profiling of Rsl1-sensitive genes in liver and WAT indicates that RSL1 accentuates sex-biased gene expression in liver but greatly diminishes it in WAT. RSL1 expression solely in liver is sufficient to limit diet-induced weight gain and suppress lipogenic genes in WAT, indicating that RSL1 balances metabolism via liver-to-adipose-tissue communication. RSL1's effects on adult physiology exemplify a significant modulatory capacity of KRAB-ZFPs, in the absence of which there is widespread metabolic dysregulation. This ability to buffer against gene expression noise, coupled with extensive individual genetic variation, highlights the enormous potential of KRAB-Zfp genes as candidate risk factors for complex diseases.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The KRAB zinc finger protein RSL1 regulates sex- and tissue-specific promoter methylation and dynamic hormone-responsive chromatin configuration.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Sep;32(18):3732-42. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00615-12. Epub 2012 Jul 16. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22801370 Free PMC article.
-
A pair of mouse KRAB zinc finger proteins modulates multiple indicators of female reproduction.Biol Reprod. 2010 Apr;82(4):662-8. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.109.080846. Epub 2009 Dec 30. Biol Reprod. 2010. PMID: 20042539 Free PMC article.
-
Regulator of sex-limitation KRAB zinc finger proteins modulate sex-dependent and -independent liver metabolism.Physiol Genomics. 2009 Jun 10;38(1):16-28. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.90391.2008. Epub 2009 Apr 7. Physiol Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19351907 Free PMC article.
-
Spotting the enemy within: Targeted silencing of foreign DNA in mammalian genomes by the Krüppel-associated box zinc finger protein family.Mob DNA. 2015 Oct 2;6:17. doi: 10.1186/s13100-015-0050-8. eCollection 2015. Mob DNA. 2015. PMID: 26435754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KRAB-ZFP Transcriptional Regulators Acting as Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors: An Overview.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 23;22(4):2212. doi: 10.3390/ijms22042212. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33672287 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ZNF26-Associated Genes as Prognostic Signatures in Colorectal Cancer with Broad Therapeutic Implications.J Appl Genet. 2025 Feb;66(1):141-153. doi: 10.1007/s13353-024-00854-3. Epub 2024 Apr 3. J Appl Genet. 2025. PMID: 38568413
-
Tissue-Specific Trans Regulation of the Mouse Epigenome.Genetics. 2019 Mar;211(3):831-845. doi: 10.1534/genetics.118.301697. Epub 2018 Dec 28. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 30593494 Free PMC article.
-
ZNF545 suppresses human hepatocellular carcinoma growth by inhibiting NF-kB signaling.Genes Cancer. 2017 Mar;8(3-4):528-535. doi: 10.18632/genesandcancer.137. Genes Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28680537 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc finger proteins in cancer progression.J Biomed Sci. 2016 Jul 13;23(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12929-016-0269-9. J Biomed Sci. 2016. PMID: 27411336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-339 inhibits human hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion via targeting ZNF689.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Jan 22;13:435-445. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S186352. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 30774308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mackay DJ, Callaway JL, Marks SM, White HE, Acerini CL, Boonen SE, Dayanikli P, Firth HV, Goodship JA, Haemers AP, Hahnemann JM, Kordonouri O, Masoud AF, Oestergaard E, Storr J, Ellard S, Hattersley AT, Robinson DO, Temple IK. 2008. Hypomethylation of multiple imprinted loci in individuals with transient neonatal diabetes is associated with mutations in ZFP57. Nat. Genet. 40:949–951. 10.1038/ng.187 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
