Gamma interferon-induced guanylate binding protein 1 is a novel actin cytoskeleton remodeling factor
- PMID: 24190970
- PMCID: PMC3911287
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00664-13
Gamma interferon-induced guanylate binding protein 1 is a novel actin cytoskeleton remodeling factor
Abstract
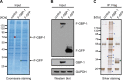
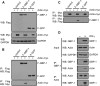
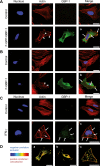
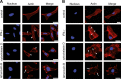
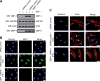
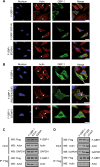
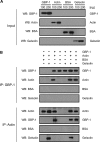
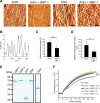
Gamma interferon (IFN-γ) regulates immune defenses against viruses, intracellular pathogens, and tumors by modulating cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and vesicle trafficking processes. The large GTPase guanylate binding protein 1 (GBP-1) is among the cellular proteins that is the most abundantly induced by IFN-γ and mediates its cell biologic effects. As yet, the molecular mechanisms of action of GBP-1 remain unknown. Applying an interaction proteomics approach, we identified actin as a strong and specific binding partner of GBP-1. Furthermore, GBP-1 colocalized with actin at the subcellular level and was both necessary and sufficient for the extensive remodeling of the fibrous actin structure observed in IFN-γ-exposed cells. These effects were dependent on the oligomerization and the GTPase activity of GBP-1. Purified GBP-1 and actin bound to each other, and this interaction was sufficient to impair the formation of actin filaments in vitro, as demonstrated by atomic force microscopy, dynamic light scattering, and fluorescence-monitored polymerization. Cosedimentation and band shift analyses demonstrated that GBP-1 binds robustly to globular actin and slightly to filamentous actin. This indicated that GBP-1 may induce actin remodeling via globular actin sequestering and/or filament capping. These results establish GBP-1 as a novel member within the family of actin-remodeling proteins specifically mediating IFN-γ-dependent defense strategies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pathophysiological role of guanylate-binding proteins in gastrointestinal diseases.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Jul 28;22(28):6434-43. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i28.6434. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27605879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IFN-γ-response mediator GBP-1 represses human cell proliferation by inhibiting the Hippo signaling transcription factor TEAD.Biochem J. 2018 Sep 25;475(18):2955-2967. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20180123. Biochem J. 2018. PMID: 30120107 Free PMC article.
-
Processing and secretion of guanylate binding protein-1 depend on inflammatory caspase activity.J Cell Mol Med. 2017 Sep;21(9):1954-1966. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13116. Epub 2017 Mar 8. J Cell Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28272793 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of guanylate binding protein 5 by gamma interferon increases susceptibility to Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium-induced pyroptosis in RAW 264.7 cells.Infect Immun. 2008 Jun;76(6):2304-15. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01437-07. Epub 2008 Mar 24. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18362138 Free PMC article.
-
Articular Chondrocyte Phenotype Regulation through the Cytoskeleton and the Signaling Processes That Originate from or Converge on the Cytoskeleton: Towards a Novel Understanding of the Intersection between Actin Dynamics and Chondrogenic Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 23;22(6):3279. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063279. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33807043 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic analysis uncovers common effects of IFN-γ and IL-27 on the HLA class I antigen presentation machinery in human cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 8;7(45):72518-72536. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12235. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27683036 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiological role of guanylate-binding proteins in gastrointestinal diseases.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Jul 28;22(28):6434-43. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i28.6434. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27605879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Guanylate-Binding Protein 1 as a Potential Predictor of Immunotherapy: A Pan-Cancer Analysis.Front Genet. 2022 Feb 10;13:820135. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.820135. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35222540 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleotide-dependent farnesyl switch orchestrates polymerization and membrane binding of human guanylate-binding protein 1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Jul 11;114(28):E5559-E5568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1620959114. Epub 2017 Jun 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28645896 Free PMC article.
-
IFN-γ drives inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis through VE-cadherin-directed vascular barrier disruption.J Clin Invest. 2019 Nov 1;129(11):4691-4707. doi: 10.1172/JCI124884. J Clin Invest. 2019. PMID: 31566580 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
