MCPIP1 restricts HIV infection and is rapidly degraded in activated CD4+ T cells
- PMID: 24191027
- PMCID: PMC3839757
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1316208110
MCPIP1 restricts HIV infection and is rapidly degraded in activated CD4+ T cells
Abstract
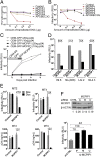
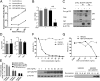
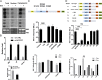
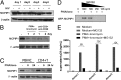
HIV-1 primarily infects activated CD4+ T cells and macrophages. Quiescent CD4+ T cells, however, possess cellular factors that limit HIV-1 infection at different postentry steps of the viral life cycle. Here, we show that the previously reported immune regulator monocyte chemotactic protein-induced protein 1 (MCPIP1) restricts HIV-1 production in CD4+ T cells. While the ectopic expression of MCPIP1 in cell lines abolished the production of HIV-1, silencing of MCPIP1 enhanced HIV-1 production. Subsequent analysis indicated that MCPIP1 imposes its restriction by decreasing the steady levels of viral mRNA species through its RNase domain. Remarkably, common T-cell stimuli induced the rapid degradation of MCPIP1 in both T-cell lines and quiescent human CD4+ T cells. Lastly, blocking the proteosomal degradation of MCPIP1 by MG132 abrogated HIV-1 production in phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate/ionomycin-stimulated human CD4+ T cells isolated from healthy donors. Overall, MCPIP1 poses a potent barrier against HIV-1 infection at a posttranscriptional stage. Although the observed HIV restriction conferred by MCPIP1 does not seem to be overcome by any viral protein, it is removed during cellular stimulation. These findings provide insights into the mechanisms of cellular activation-mediated HIV-1 production in CD4+ T cells.
Keywords: antiviral immunity; restriction factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sheehy AM, Gaddis NC, Choi JD, Malim MH. Isolation of a human gene that inhibits HIV-1 infection and is suppressed by the viral Vif protein. Nature. 2002;418(6898):646–650. - PubMed
-
- Harris RS, et al. DNA deamination mediates innate immunity to retroviral infection. Cell. 2003;113(6):803–809. - PubMed
-
- Mangeat B, et al. Broad antiretroviral defence by human APOBEC3G through lethal editing of nascent reverse transcripts. Nature. 2003;424(6944):99–103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

