A novel mouse model of pediatric cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation reveals age-dependent neuronal sensitivities to ischemic injury
- PMID: 24192226
- PMCID: PMC3919447
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2013.10.015
A novel mouse model of pediatric cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation reveals age-dependent neuronal sensitivities to ischemic injury
Abstract
Background: Pediatric sudden cardiac arrest (CA) is an unfortunate and devastating condition, often leading to poor neurologic outcomes. However, little experimental data on the pathophysiology of pediatric CA is currently available due to the scarcity of animal models.
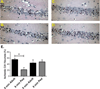
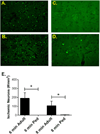
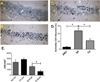
New method: We developed a novel experimental model of pediatric cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CA/CPR) using postnatal day 20-25 mice. Adult (8-12 weeks) and pediatric (P20-25) mice were subjected to 6min CA/CPR. Hippocampal CA1 and striatal neuronal injury were quantified 3 days after resuscitation by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and Fluoro-Jade B staining, respectively.
Results: Pediatric mice exhibited less neuronal injury in both CA1 hippocampal and striatal neurons compared to adult mice. Increasing ischemia time to 8 min CA/CPR resulted in an increase in hippocampal injury in pediatric mice, resulting in similar damage in adult and pediatric brains. In contrast, striatal injury in the pediatric brain following 6 or 8 min CA/CPR remained extremely low. As observed in adult mice, cardiac arrest causes delayed neuronal death in pediatric mice, with hippocampal CA1 neuronal damage maturing at 72 h after insult. Finally, mild therapeutic hypothermia reduced hippocampal CA1 neuronal injury after pediatric CA/CPR.
Comparison with existing method: This is the first report of a cardiac arrest and CPR model of global cerebral ischemia in mice.
Conclusions: Therefore, the mouse pediatric CA/CPR model we developed is unique and will provide an important new tool to the research community for the study of pediatric brain injury.
Keywords: Cardiac arrest; Global cerebral ischemia; Hypothermia; Juvenile; Pediatric.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- The Hypotherrmia after Cardiac Arrest Study Group. Mild therapeutic hypothermia to improve the neurologic outcome after cardiac arrest. The New England journal of medicine. 2002;346:549–556. - PubMed
-
- Abe K, Aoki M, Kawagoe J, Yoshida T, Hattori A, Kogure K, Itoyama Y. Ischemic delayed neuronal death. A mitochondrial hypothesis. Stroke. 1995;26:1478–1489. - PubMed
-
- Anderson V, Spencer-Smith M, Wood A. Do children really recover better? Neurobehavioural plasticity after early brain insult. Brain. 2011;134:2197–2221. - PubMed
-
- Arrich J, Holzer M, Havel C, Mullner M, Herkner H. Hypothermia for neuroprotection in adults after cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;9:CD004128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

