p53 regulates the transcription of the anti-inflammatory molecule developmental endothelial locus-1 (Del-1)
- PMID: 24192518
- PMCID: PMC3875763
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.1318
p53 regulates the transcription of the anti-inflammatory molecule developmental endothelial locus-1 (Del-1)
Abstract
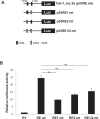
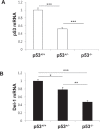
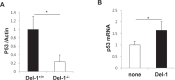
Developmental endothelial locus-1 (Del-1) is an endothelium-derived anti-inflammatory molecule that is downregulated by inflammatory stimuli. Little is known about the molecular mechanisms by which Del-1 transcription is regulated. In the present study, a DNA sequence upstream of the Del-1 gene was analyzed and putative p53 response elements (p53REs) were identified. An approximately 2 kb fragment upstream of the translation start site displayed the highest Del-1 transcriptional activity, and the transcriptional activity of this fragment was enhanced by overexpression of p53. Chemical activation of endogenous p53 elevated the levels of Del-1 mRNA. Site-directed mutagenesis of CATG in the consensus sequences of the 2 kb fragment to TATA significantly reduced the transcription of Del-1. Chromatin immunoprecipitation revealed recruitment of p53 to the p53REs of the Del-1 promoter, resulting in increased Del-1 transcription. Finally, primary endothelial cells isolated from mice with reduced levels of p53 showed a decrease in Del-1 mRNA compared to wild-type endothelial cells. Moreover, Del-1 reciprocally enhanced p53 expression in primary endothelial cells. Thus, these findings suggest that Del-1 is a novel transcriptional target gene of p53.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Hidai C, Zupancic T, Penta K, Mikhail A, Kawana M, Quertermous EE, Aoka Y, Fukagawa M, Matsui Y, Platika D, Auerbach R, Hogan BL, Snodgrass R, Quertermous T. Cloning and characterization of developmental endothelial locus-1: an embryonic endothelial cell protein that binds the alphavbeta3 integrin receptor. Genes Dev. 1998;12(1):21–33. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kitano H, Kokubun S, Hidai C. The extracellular matrix protein Del1 induces apoptosis via its epidermal growth factor motif. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;393(4):757–761. - PubMed
-
- Rezaee M, Penta K, Quertermous T. Del1 mediates VSMC adhesion, migration, and proliferation through interaction with integrin alpha(v)beta(3) Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2002;282(5):H1924–1932. - PubMed
-
- Wang Z, Kundu RK, Longaker MT, Quertermous T, Yang GP. The angiogenic factor Del1 prevents apoptosis of endothelial cells through integrin binding. Surgery. 2012;151(2):296–305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

