Rho-kinase inhibition improves ischemic perfusion deficit in hyperlipidemic mice
- PMID: 24192634
- PMCID: PMC3915205
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2013.195
Rho-kinase inhibition improves ischemic perfusion deficit in hyperlipidemic mice
Abstract
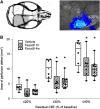
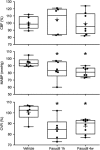
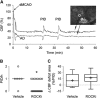
Hyperlipidemia is a major cardiovascular risk factor associated with progressive cerebrovascular dysfunction and diminished collateral perfusion in stroke. Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) may be an important mediator of hyperlipidemic vascular dysfunction. We tested the efficacy of acute or chronic ROCK inhibition on the size of dynamic perfusion defect using laser speckle flowmetry in hyperlipidemic apolipoprotein E knockout mice fed on a high-fat diet for 8 weeks. Mice were studied at an age before the development of flow-limiting atherosclerotic stenoses in aorta and major cervical arteries. Focal ischemia was induced by distal middle cerebral artery occlusion (dMCAO) during optical imaging. The ROCK inhibitor fasudil (10 mg/kg) was administered either as a single dose 1 hour before ischemia onset, or daily for 4 weeks. Fasudil decreased both baseline arterial blood pressure and cerebrovascular resistance (CVR) by ∼15%, and significantly improved tissue perfusion during dMCAO. Interestingly, peri-infarct depolarizations were also reduced. Chronic treatment did not further enhance these benefits compared with acute treatment with a single dose. These data show that ROCK inhibition improves CVR and ischemic tissue perfusion in hyperlipidemic mice.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rho-kinase inhibition acutely augments blood flow in focal cerebral ischemia via endothelial mechanisms.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007 May;27(5):998-1009. doi: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600406. Epub 2006 Oct 11. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007. PMID: 17033691 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Rho kinase (ROCK) leads to increased cerebral blood flow and stroke protection.Stroke. 2005 Oct;36(10):2251-7. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000181077.84981.11. Epub 2005 Sep 1. Stroke. 2005. PMID: 16141422 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperlipidemia disrupts cerebrovascular reflexes and worsens ischemic perfusion defect.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013 Jun;33(6):954-62. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2013.38. Epub 2013 Mar 13. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013. PMID: 23486293 Free PMC article.
-
Pleiotropic effects of the rho-kinase inhibitor fasudil after subarachnoid hemorrhage: a review of preclinical and clinical studies.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2014;12(5):758-65. doi: 10.2174/1570161112666140613115813. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24923440 Review.
-
Current status of rho-associated kinases (ROCKs) in coronary atherosclerosis and vasospasm.Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2009 Oct;7(4):322-30. doi: 10.2174/187152509789541891. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19607644 Review.
Cited by
-
Improving Reperfusion Therapies in the Era of Mechanical Thrombectomy.Transl Stroke Res. 2016 Aug;7(4):294-302. doi: 10.1007/s12975-016-0469-3. Epub 2016 May 24. Transl Stroke Res. 2016. PMID: 27221511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Refined Ischemic Penumbra Imaging with Tissue pH and Diffusion Kurtosis Magnetic Resonance Imaging.Transl Stroke Res. 2021 Oct;12(5):742-753. doi: 10.1007/s12975-020-00868-z. Epub 2020 Nov 7. Transl Stroke Res. 2021. PMID: 33159656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rho-kinase inhibitors do not expand hematoma volume in acute experimental intracerebral hemorrhage.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2018 May 1;5(6):769-776. doi: 10.1002/acn3.569. eCollection 2018 Jun. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29928660 Free PMC article.
-
The cross-talk between canonical and non-canonical Wnt-dependent pathways regulates P-glycoprotein expression in human blood-brain barrier cells.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2014 Aug;34(8):1258-69. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2014.100. Epub 2014 Jun 4. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2014. PMID: 24896565 Free PMC article.
-
Thomas Willis Lecture: Targeting Brain Arterioles for Acute Stroke Treatment.Stroke. 2021 Jul;52(7):2465-2477. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.034620. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Stroke. 2021. PMID: 34102855 Free PMC article.
References
-
- d'Uscio LV, Smith LA, Katusic ZS. Hypercholesterolemia impairs endothelium-dependent relaxations in common carotid arteries of apolipoprotein e-deficient mice. Stroke. 2001;32:2658–2664. - PubMed
-
- Casino PR, Kilcoyne CM, Quyyumi AA, Hoeg JM, Panza JA. The role of nitric oxide in endothelium-dependent vasodilation of hypercholesterolemic patients. Circulation. 1993;88:2541–2547. - PubMed
-
- Kitayama J, Faraci FM, Lentz SR, Heistad DD. Cerebral vascular dysfunction during hypercholesterolemia. Stroke. 2007;38:2136–2141. - PubMed
-
- Morikage N, Kishi H, Sato M, Guo F, Shirao S, Yano T, et al. Cholesterol primes vascular smooth muscle to induce Ca2 sensitization mediated by a sphingosylphosphorylcholine-Rho-kinase pathway: possible role for membrane raft. Circ Res. 2006;99:299–306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

