Inhibition of elastin peptide-mediated angiogenic signaling mechanism(s) in choroidal endothelial cells by the α6(IV)NC1 collagen fragment
- PMID: 24194191
- PMCID: PMC3867182
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.12-10870
Inhibition of elastin peptide-mediated angiogenic signaling mechanism(s) in choroidal endothelial cells by the α6(IV)NC1 collagen fragment
Abstract
Purpose: The inhibitory effects and mechanism(s) of type IV collagen α-6 chain-derived noncollagenous domain (α6[IV]NC1 or hexastatin) on elastin-derived peptide (EDP)-activated choroidal endothelial cell migration, kinase signaling, and membrane type 1 metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) activation are explored.
Methods: Mouse choroidal endothelial cells (MCECs) were incubated in media with soluble EDPs (kappa elastin, mouse elastin, and Val-Gly-Val-Ala-Pro-Gly [VGVAPG] hexapeptide) for different time intervals with or without α6(IV)NC1. The MCECs proliferation, migration, tube formation, MT1-MMP expression, and angiogenic signaling were analyzed in cells subjected to EDP and α6(IV)NC1 treatments. The MCECs also were subjected to EDPs, and specific inhibitors for evaluation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and protein kinase B (Akt) phosphorylation.
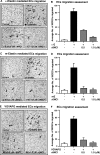
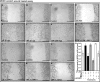
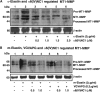
Results: Kappa elastin, mouse elastin, and VGVAPG enhanced the migration, without affecting the proliferation of MCECs. The α6(IV)NC1 inhibited survival and EDP-activated migration of MCECs. The EDP-activated MCEC tube formation on matrigel also was inhibited by α6(IV)NC1. Further, EDP-activated MT1-MMP expression and FAK/phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI-3K)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mToR)/Akt phosphorylation in MCECs, were reduced by α6(IV)NC1. The EDP-induced FAK and Akt phosphorylation was blocked by FAK- and Akt-specific inhibitors.
Conclusions: The EDPs and α6(IV)NC1 are identified to exhibit opposing effects on MCEC angiogenic behavior and signaling. The α6(IV)NC1 inhibited cell survival, EDP-mediated migration, MT1-MMP expression and, FAK/PI-3K/mToR/Akt phosphorylation in MCECs. This work demonstrates α6(IV)NC1 as a prospective endogenous molecule for the treatment of diseases involving choroidal neovascularization in the eye.
Keywords: angiogenesis; elastin-derived peptides; noncollagenous domains of type IV collagen.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Developments in purification methods for obtaining and evaluation of collagen derived endogenous angioinhibitors.Protein Expr Purif. 2014 Feb;94:46-52. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2013.10.021. Epub 2013 Nov 9. Protein Expr Purif. 2014. PMID: 24215863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular responses of choroidal endothelial cells to elastin derived peptides through the elastin-binding protein (GLB1).Matrix Biol. 2012 Mar;31(2):113-9. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2011.11.003. Epub 2011 Dec 2. Matrix Biol. 2012. PMID: 22178079 Free PMC article.
-
FAK and p38-MAP kinase-dependent activation of apoptosis and caspase-3 in retinal endothelial cells by alpha1(IV)NC1.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009 Oct;50(10):4567-75. doi: 10.1167/iovs.09-3473. Epub 2009 May 14. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009. PMID: 19443723 Free PMC article.
-
Elastin-derived peptides enhance angiogenesis by promoting endothelial cell migration and tubulogenesis through upregulation of MT1-MMP.J Cell Sci. 2005 Jan 15;118(Pt 2):343-56. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01613. Epub 2005 Jan 4. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 15632106
-
Type XIX collagen: A new partner in the interactions between tumor cells and their microenvironment.Matrix Biol. 2017 Jan;57-58:169-177. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2016.07.010. Epub 2016 Aug 1. Matrix Biol. 2017. PMID: 27491275 Review.
Cited by
-
Type IV collagen α1-chain noncollagenous domain blocks MMP-2 activation both in-vitro and in-vivo.Sci Rep. 2014 Mar 26;4:4136. doi: 10.1038/srep04136. Sci Rep. 2014. Retraction in: Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 26;10(1):20995. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-76500-9. PMID: 24670518 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Developments in purification methods for obtaining and evaluation of collagen derived endogenous angioinhibitors.Protein Expr Purif. 2014 Feb;94:46-52. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2013.10.021. Epub 2013 Nov 9. Protein Expr Purif. 2014. PMID: 24215863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extra cellular matrix derived metabolite regulates angiogenesis by FasL mediated apoptosis.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 4;8(12):e80555. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080555. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24324608 Free PMC article.
-
Elastin-derived peptides (EDPs) as a potential pro-malignancy factor in human leukemia cell lines.Immunol Res. 2024 Oct;72(5):1092-1107. doi: 10.1007/s12026-024-09511-7. Epub 2024 Jul 5. Immunol Res. 2024. PMID: 38967692 Free PMC article.
-
The Elastin Receptor Complex: A Unique Matricellular Receptor with High Anti-tumoral Potential.Front Pharmacol. 2016 Mar 4;7:32. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00032. eCollection 2016. Front Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26973522 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Guymer RH, Bird AC, Hageman GS. Cytoarchitecture of choroidal capillary endothelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004; 45: 1660–1666 - PubMed
-
- Sivaprasad S, Chong NV, Bailey TA. Serum elastin-derived peptides in age-related macular degeneration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005; 46: 3046–3051 - PubMed
-
- Kielty CM, Sherratt MJ, Shuttleworth CA. Elastic fibres. J Cell Sci. 2002; 115: 2817–2828 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

