Pimozide for schizophrenia or related psychoses
- PMID: 24194433
- PMCID: PMC11927953
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001949.pub3
Pimozide for schizophrenia or related psychoses
Abstract
Background: Pimozide, formulated in the 1960s, continues to be marketed for the care of people with schizophrenia or related psychoses such as delusional disorder. It has been associated with cardiotoxicity and sudden unexplained death. Electrocardiogram monitoring is now required before and during use.
Objectives: To review the effects of pimozide for people with schizophrenia or related psychoses in comparison with placebo, no treatment or other antipsychotic medication.A secondary objective was to examine the effects of pimozide for people with delusional disorder.
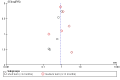
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group's Register (28 January 2013).
Selection criteria: We sought all relevant randomised clinical trials (RCTs) comparing pimozide with other treatments.
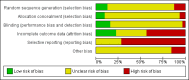
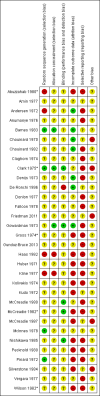
Data collection and analysis: Working independently, we inspected citations, ordered papers and then re-inspected and assessed the quality of the studies and of extracted data. For homogeneous dichotomous data, we calculated the relative risk (RR), the 95% confidence interval (CI) and mean differences (MDs) for continuous data. We excluded data if loss to follow-up was greater than 50%. We assessed risk of bias for included studies and used GRADE to rate the quality of the evidence.
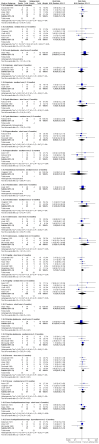
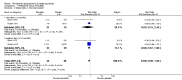
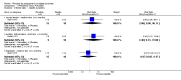
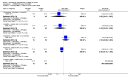
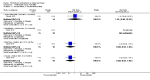
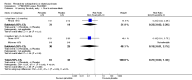
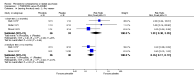
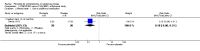
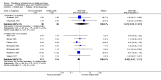
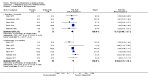
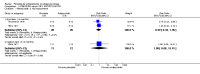
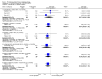
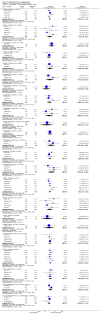
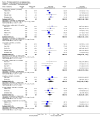
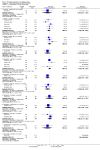
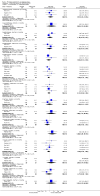
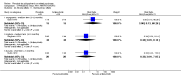
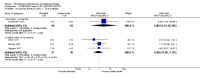
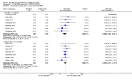
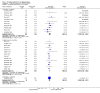
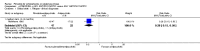
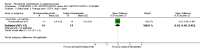
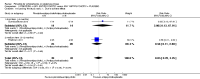
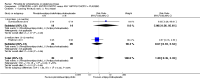
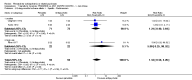
Main results: We included 32 studies in total: Among the five studies that compared pimozide versus placebo, only one study provided data for global state relapse, for which no difference between groups was noted at medium term (1 RCT n = 20, RR 0.22 CI 0.03 to 1.78, very low quality of evidence). None of the five studies provided data for no improvement or first-rank symptoms in mental state. Data for extrapyramidal symptoms demonstrate no difference between groups for Parkinsonism (rigidity) at short term (1 RCT, n = 19, RR 5.50 CI 0.30 to 101.28, very low quality of evidence) or at medium term (1 RCT n = 25, RR 1.33 CI 0.14 to 12.82, very low quality of evidence), or for Parkinsonism (tremor) at medium term (1 RCT n = 25, RR 1 CI 0.2 to 4.95, very low quality of evidence). No data were reported for quality of life at medium term.Of the 26 studies comparing pimozide versus any antipsychotic, seven studies provided data for global state relapse at medium term, for which no difference was noted (7 RCTs n = 227, RR 0.82 CI 0.57 to 1.17, moderate quality of evidence). Data from one study demonstrated no difference in mental state (no improvement) at medium term (1 RCT n = 23, RR 1.09 CI 0.08 to 15.41, very low quality evidence); another study demonstrated no difference in the presence of first-rank symptoms at medium term (1 RCT n = 44, RR 0.53 CI 0.25 to 1.11, low quality of evidence). Data for extrapyramidal symptoms demonstrate no difference between groups for Parkinsonism (rigidity) at short term (6 RCTs n = 186, RR 1.21 CI 0.71 to 2.05,low quality of evidence) or medium term (5 RCTs n = 219, RR 1.12 CI 0.24 to 5.25,low quality of evidence), or for Parkinsonism (tremor) at medium term (4 RCTs n = 174, RR 1.46 CI 0.68 to 3.11, very low quality of evidence). No data were reported for quality of life at medium term.In the one study that compared pimozide plus any antipsychotic versus the same antipsychotic, significantly fewer relapses were noted in the augmented pimozide group at medium term (1 RCT n = 69, RR 0.28 CI 0.15 to 0.50, low quality evidence). No data were reported for mental state outcomes or for extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS). Data were skewed for quality of life scores, which were not included in the meta-analysis but were presented separately.Two studies compared pimozide plus any antipsychotics versus antipsychotic plus placebo; neither study reported data for outcomes of interest, apart from Parkinsonism at medium term and quality of life using the Specific Level of Functioning scale (SLOF); however, data were skewed.Only one study compared pimozide plus any antipsychotic versus antipsychotics plus antipsychotic; no data were reported for global state and mental state outcomes of interest. Data were provided for Parkinsonism (rigidity and tremor) using the Extrapyramidal Symptom Rating Scale (ESRS); however, these data were skewed.
Authors' conclusions: Although shortcomings in the data are evident, enough overall consistency over different outcomes and time scales is present to confirm that pimozide is a drug with efficacy similar to that of other, more commonly used antipsychotic drugs such as chlorpromazine for people with schizophrenia. No data support or refute its use for those with delusional disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures

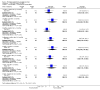
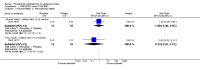
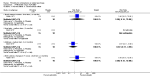
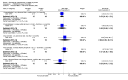











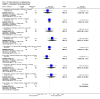
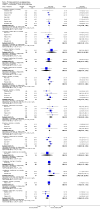
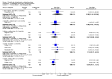
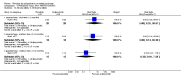



















Update of
-
Pimozide for schizophrenia or related psychoses.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jul 18;(3):CD001949. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001949.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Nov 05;(11):CD001949. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001949.pub3. PMID: 17636692 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Abuzzahab 1980* {published data only}
-
- Abuzzahab FS Sr. Evaluations of social functioning in a 3‐year double‐blind investigation of pimozide versus fluphenazine in chronic schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1977;13:71‐3. - PubMed
-
- Abuzzahab FS Sr, Zimmermann RL. A three‐year double‐blind investigation of pimozide versus fluphenazine in chronic schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1976;12:26‐7. - PubMed
-
- Abuzzahab FS, Zimmermann RL. Factors determining patient tenure on a 3‐year double‐blind investigation of pimozide versus fluphenazine HCl. Advances in Biochemistry and Psychopharmacology 1980;24:547‐50. - PubMed
Amin 1977 {published data only}
-
- Amin MM, Ban TA, Lehmann HE. A standard (trifluoperazine) controlled clinical study with pimozide in the maintenance treatment of schizophrenic patients. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1977;13:15‐7. - PubMed
Andersen 1972 {published data only}
-
- Andersen K, d'Elia G, Hallberg B, Perris C, Rapp W, Roman G. A controlled trial of pimozide and trifluoperazine in chronic schizophrenic syndromes. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica Supplementum 1974;249:43‐64. - PubMed
Anumonye 1976 {published data only}
-
- Anumonye A, Onibuwe‐Johnson T, Marinho AA. Clinical trial of pimozide. West African Journal of Pharmacology and Drug Research 1976;3:17‐24. - PubMed
Barnes 1983 {published data only}
-
- Barnes TR, Milavic G, Curson DA, Platt SD. Use of the Social Behaviour Assessment Schedule (SBAS) in a trial of maintenance antipsychotic therapy in schizophrenic outpatients: pimozide versus fluphenazine. Social Psychiatry 1983;18:193‐9. - PubMed
-
- Barnes TR, Platt SD. E‐mail correspondence. E‐mail correspondence June 2011.
Chouinard 1970 {published data only}
-
- Chouinard G, Lehmann HE, Ban TA. Pimozide in the treatment of chronic schizophrenic patients. Current Therapeutic Research and Clinical Experience 1970;12:598‐603. - PubMed
Chouinard 1982 {published data only}
-
- Chouinard GR, Annable L. Pimozide in the treatment of newly admitted schizophrenic patients. Psychopharmacology 1982;76:13‐9. - PubMed
Claghorn 1974 {published data only}
-
- Claghorn JL. A double blind comparison of pimozide vs. trifluoperazine in schizophrenic outpatients. Current Therapeutic Research 1974;16:1005‐9. - PubMed
Clark 1975* {published data only}
-
- Clark ML. Pimozide vs thioridazine vs placebo. Early Clinical Drug Evaluation Unit Reports 1973; Vol. 9.
-
- Clark ML, Huber WK, Hill D, Wood F, Costiloe JP. Pimozide in chronic schizophrenic outpatients. Diseases of the Nervous System 1975;36:137‐41. - PubMed
Denijs 1973 {published data only}
-
- Denijs EL, Vereecken JL. Pimozide (orap, R 6238) in residual schizophrenia: a clinical evaluation with long‐term double‐blind follow‐up. Psychiatria Neurologia Neurochirurgia 1973;76:47‐59. - PubMed
De Ronchi 1996 {published data only}
-
- Ronchi D. Levosulpiride vs pimozide in negative symptoms of schizophrenia. Proceedings of the Xth World Congress of Psychiatry; August 23‐28, 1996; Madrid, Spain. 1996.
-
- Ronchi D, Belelli G, Ruggeri M, Linari F, Tonti L, Volterra V. Levosulpiride vs pimozide in schizophrenic patients: efficacy and adverse events [Levosulpiride vs pimozide in pazienti schizofrenici: efficacia ed eventi avversi]. Neurologia Psichiatria Scienze Umane 1997;17(6):859‐73. [EMBASE: 1998134063]
-
- Ronchi D, Ruggeri M, Balelli G, Volterra V. Levosulpiride vs pimozide in negative symptoms of schizophrenia. Proceedings of the 8th ECNP (European College of Neuropsychopharmacology) Congress; September 30‐October 4, 1995; Venice, Italy. 1995.
-
- Ronchi D, Ruggeri M, Belelli G, Volterra V. Levosulpiride versus pimozide in negative symptoms of schizophrenia. Current Therapeutic Research ‐ Clinical and Experimental 1996;57:797‐810.
Donlon 1977 {published data only}
-
- Donlon PT, Swaback DO, Osborne ML. Pimozide versus fluphenazine in ambulatory schizophrenics: a 12‐month comparison study. Diseases of the Nervous System 1977;38:119‐23. - PubMed
Falloon 1978 {published data only}
-
- Falloon I, Watt DC, Shepherd M. A comparative controlled trial of pimozide and fluphenazine decanoate in the continuation therapy of schizophrenia. Psychological Medicine 1978;8:59‐70. - PubMed
-
- Falloon I, Watt DC, Shepherd M. The social outcome of patients in a trial of long‐term continuation therapy. Psychological Medicine 1978;8:265‐74. - PubMed
-
- Shepherd M. Medico‐social evaluation of the long term pharmacotherapy of schizophrenia: comparaive study of fluphenazine and pimozide. Progressive Neuro‐Psychopharmacology 1979;3:383‐9. - PubMed
Friedman 2011 {published data only}
Gowardman 1973 {published data only}
-
- Gowardman M, Barrer B, Brown RA. Pimozide (R6238) in chronic schizophrenia: double blind trial. New Zealand Medical Journal 1973;78:487‐91. - PubMed
Gross 1974* {published data only}
-
- Gross‐HS. A double‐blind comparison of once‐a‐day pimozide, trifluoperazine, and placebo in the maintenance care of chronic schizophrenic outpatients. Current Therapeutic Research and Clinical Experience 1974;16:696‐705. - PubMed
Gunduz‐Bruce 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Gunduz‐Bruce H. Efficacy of pimozide augmentation for clozapine partial response. Clinicaltrials.gov. [NCT00374244] - PubMed
-
- Gunduz‐Bruce H, Oliver S, Gueorguieva R, Forselius‐Bielen K, D'Souza DC, Zimolo Z, et al. Efficacy of pimozide augmentation for clozapine partial responders with schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 2013;143:344‐7. - PubMed
Haas 1982 {published data only}
-
- Haas S, Beckmann H. Pimozide versus haloperidol in acute schizophrenia: a double blind controlled study. Pharmacopsychiatria 1982;15:70‐4. - PubMed
Huber 1971 {published data only}
-
- Huber W, Serafetinides EA, Colmore JP, Clark M. Pimozide in chronic schizophrenic patients. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and New Drugs 1971;11:304‐9. - PubMed
Kline 1977 {published data only}
-
- Kline F, Burgoyne RW, Yamamoto J. Comparison of pimozide and trifluoperazine as once‐daily therapy in chronic schizophrenic outpatients. Current Therapeutic Research 1977;21:768‐78.
Kolivakis 1974 {published data only}
-
- Kolivakis T, Azim H, Kingstone E. A double‐blind comparison of pimozide and chlorpromazine in the maintenance care of chronic schizophrenic outpatients. Current Therapeutic Research 1974;16:998‐1004. - PubMed
Kudo 1972 {published data only}
-
- Kudo Y. A double blind comparison of pimozide with carpipramine in schizophrenic patients. Acta Psychiatrica Belgica 1972;72:685‐97. - PubMed
-
- Kudo Y, Fujiki A, Hino S, Kobayashi Y, Nagasaka G, Saitoh Y, et al. The double‐blind study of pimozide for schizophrenia. Igaku No Ayumi 1972;82(11):726‐37. [MEDLINE: ; PMID 2694767]
McCreadie 1980 {published data only}
-
- McCreadie R, Dingwall J, Wiles D, Heykants J. Intermittent pimozide versus fluphenazine decanoate as maintenance therapy in chronic schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 1980;137:510‐7. - PubMed
McCreadie 1982* {published data only}
-
- McCreadie R, Mackie M, Morrison D, Kidd J. Once weekly pimozide versus fluphenazine decanoate as maintenance therapy in chronic schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 1982;140:280‐6. - PubMed
McCreadie 1987 {published data only}
-
- Scottish Schizophrenia Research Group. The Scottish First Episode Schizophrenia Study. VIII. Five‐year follow‐up: clinical and psychosocial findings. British Journal of Psychiatry 1992;161:496‐500. - PubMed
-
- Scottish Schizophrenia Research Group: McCreadie RG, Wiles D, Grant S, Crocket GT, Mahmood Z, Livingston MG, et al. The Scottish First Episode Schizophrenia Study. VII. Two‐year follow up. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1989;80:597‐602. - PubMed
-
- The Scottish Schizophrenia Research Group. The Scottish First Episode Schizophrenia Study. II. Treatment: pimozide versus flupenthixol. British Journal of Psychiatry 1987;150:334‐8. - PubMed
-
- The Scottish Schizophrenia Research Group. The Scottish First Episode Schizophrenia Study. III. Cognitive performance. British Journal of Psychiatry 1987;150:338‐40. - PubMed
-
- The Scottish Schizophrenia Research Group. The Scottish First Episode Schizophrenia Study: one‐year follow‐up. British Journal of Psychiatry 1988;152:470‐6. - PubMed
McInnes 1978 {published data only}
-
- McInnes EJ, Walker F, Snelling E. The observer interaction variable in evaluation of socialising properties of pimozide (Orap). New Zealand Medicine Journal 1978;87:170‐2. - PubMed
Nishikawa 1985 {published data only}
-
- Nishikawa T, Tsuda A, Tanaka M, Koga I, Uchida Y. Prophylactic effects of neuroleptics in symptom‐free schizophrenics: roles of dopaminergic and noradrenergic blockers. Biological Psychiatry 1985;20:1161‐6. - PubMed
Pecknold 1980 {published data only}
-
- Pecknold JC, McClure DJ, Allan T, Wrzesinski L. Comparison of pimozide and chlorpromazine in acute schizophrenia. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry 1982;27:208‐12. - PubMed
Pinard 1972 {published data only}
-
- Pinard G, Prenoveau Y, Fielsen W, Elie R, Bielman P, Lamontagne Y, et al. [Le pimozide et la reintegration sociale des schizophrenes chroniques]. Proceedings of the World Congress of Psychiatry, 28 November‐4 December 1971; Ciudad de Mexico. 1971; Vol. 952.
-
- Pinard G, Prenoveau Y, Fliesen W, Elie R, Bielmann P, Lamontagne Y, et al. Pimozide: a comparative study in the treatment of chronic schizophrenic patients. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1972;6:22‐7. - PubMed
Silverstone 1984 {published data only}
-
- Silverstone T, Cookson J, Ball R, et al. The relationship of dopamine receptor blockade to clinical response in schizophrenic patients treated with pimozide or haloperidol. Journal of Psychiatric Research 1984;18:255‐68. - PubMed
Vergara 1977 {published data only}
-
- Vergara L, Amin MM, Ban TA. A standard (trifluoperazine) controlled clinical study with pimozide in the maintenance treatment of schizophrenic patients. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1977;13:17‐9. - PubMed
Wilson 1982* {published data only}
-
- Wilson LG, Roberts RW, Gerber CJ, Johnson MH. Pimozide versus chlorpromazine in chronic schizophrenia, a 52‐week double‐blind study of maintenance therapy. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1982;43:62‐5. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Baggio 1970 {published data only}
-
- Baggio MA, Dias VS. Pimozide (R6238): clinical tests with a new incisive neuroleptic of long lasting action. Revista Brasileira Psiquiatrica 1970;4(4):189‐93.
Baro 1972 {published data only}
-
- Baro F, Lommel R, Dom R, Mesmaecker L. Pimozide treatment of chronic schizophrenics as compared with haloperidol and penfluridol maintenance treatment-a multidisciplinary approach. Acta Psychiatrica Belgica 1972;72:199‐214. - PubMed
Bobon 1968 {published data only}
-
- Bobon J, Collard J, Pinchard A, Goffioul L, Bobon DP, Devroye A. No English title available [Neuroleptiques a longue duree d'action II Etude de pilote du pimozide (R6238)]. Acta Neurologica Belgiana 1968;68:137‐53. - PubMed
-
- DP Bobon, Devroye A, Goffioul L, Pinchard A. No English title available [Le pimozide: seize mois de follow up]. Acta Neurologica Belgiana 1968;68:888‐94. - PubMed
Brugmans 1968 {published data only}
-
- Brugmans J. A multicentric clinical evaluation of pimozide: preliminary report. Acta Neurologica Psychiatrica Belgica 1968;68:875‐87. - PubMed
-
- Janssen P, Brugmans J, Dony J, Schuermans V. An international double‐blind clinical evaluation of pimozide. Journal Clinical Pharmacology and New Drugs 1972;12:26‐34. - PubMed
Cetin 2000 {published data only}
-
- Cetin M, Ebrinc S. Risperidone versus pimozide for the treatment of monosymptomatic hypochondriacal psychosis. Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 2000;10(3):s325.
Cheadle 1979 {published data only}
-
- Cheadle AJ, Freeman HL. Pimozide in the maintenance treatment of apathetic and emotionally withdrawn schizophrenics. Current Medical Research and Opinion 1979;6(1):35‐43. - PubMed
Chouinard 1979 {published data only}
-
- Chouinard G, Annabel L, Lafontaine HL. Pimozide in the treatment of acute schizophrenia. Proceedings of the 132nd Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 1979 May 12‐18; Chicago, Illinois, USA. 1979.
Clark 1971 {published data only}
-
- Clark M. Pimozide versus placebo. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1971;7(1):35‐7.
Crow 1986 {published data only}
-
- Crow TJ, MacMillan JF, Johnson AL, Johnstone EC. II. A randomised controlled trial of prophylactic neuroleptic treatment. British Journal of Psychiatry 1986;148:120‐7. - PubMed
-
- Johnstone EC, Owens DGC. Does early treatment have an effect on outcome?. Proceedings of the 10th European College of Neuropharmacology Congress; September 13‐17, 1997; Vienna, Austria. 1997.
-
- MacMillan JF, Crow TJ, Johnson AL, Johnstone EC. III. Short‐term outcome in trial entrants and trial eligible patients. British Journal of Psychiatry 1986;148:128‐33. - PubMed
d'Elia 1974 {published data only}
-
- d'Elia G, Perris C, Rapp W. Objective evaluation of EEG amplitude in chronic schizophrenic patients during a controlled trial of pimozide and trifluoperazine. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica Supplementum 1974;249:78‐86. - PubMed
Feinberg 1988 {published data only}
-
- Feinberg SS, Stanley RK, Eliijovich LR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA. Pimozide treatment of the negative schizophrenic syndrome: an open trial. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1988;49(6):235‐8. - PubMed
Friedman 1997 {published data only}
-
- Friedman J, Ault K, Powchik P. Pimozide augmentation for the treatment of schizophrenic patients who are trial responders to clozapine. Biological Psychiatry 199715;42:522‐3. - PubMed
Frussa Filho 1988 {published data only}
-
- Frussa Filho R, Palermo Neto J. No English title available [Sobre os efeitos colaterais extrapyramidais dos neurolepticos]. Farmacologia Clinica 1988;96(6):389‐92.
Garton 1979 {published data only}
-
- Garton D, Silverstone T. Pimozide in acute schizophrenia: a pilot study. Current Medical Research Opinion 1979;5:799‐806. - PubMed
Gomez Perez 1994 {published data only}
-
- Gomez Perez JC. No English title available [Dismorfofobia: Pasado y presente de un trastorno centenario]. Actas Luso‐Espanol Neurologia Psiquiatria 1994;22(2):83‐8. - PubMed
Hass 1982 {published data only}
-
- Haas S, Beckmann H. Pimozide and haloperidol in a double‐blind study in acutely schizophrenic patients. Arzneimittel Forschung 1982;32(8):888.
Holl 1992 {published data only}
-
- Holl R. Nebenwirkungen von neuroleptika. Nervenheeikunde 1992;11:138‐41.
Huber 1983 {published data only}
-
- Huber G. Long‐term treatment of schizophrenia [Langzeitherapie der schizophrenie]. Medizinische Klinik 1983;78:604‐11.
Ibarra 1996 {published data only}
-
- Ibarra HS, Concha SJ, Coronel AR, Cruz PR, Alarcon NA. Pimozide in the treatment of delusional disorder. Proceedings of the 10th World Congress of Psychiatry; 1996 Aug 23‐28; Madrid, Spain. 1996.
Johnstone 1997 {published data only}
-
- Johnstone EC, Crow TJ, Frith CD, Owens DG. The Northwick park "functional" psychosis study: diagnosis and treatment response. Lancet 1988;2:119‐25. - PubMed
Kenway 1971 {published data only}
-
- Kenway AK, Masheter HC. Pimozide compared with fluphenazine in schizophrenia. British Journal of Clinical Practice 1971;25:69‐72. - PubMed
Kenway 1973 {published data only}
-
- Kenway AK. A double‐blind comparison of pimozide and haloperidol in the treatment of recurrent anxiety states. British Journal of Clinical Practice 1973;27:67‐8. - PubMed
Konig 1971 {published data only}
-
- Konig L, Lange E, Mucha H, Winkler J, Kunath B. No English title available [Klinische Moglichkeiten der Therapiebeurteilung in der Pharmakotherapie am Beissspel der Wirksamkeitsprufung eines neuen Langzeit Neuroleptikums pimozide]. Psychiatry Neurology Medicine and Psychology 1971;23:359‐67. - PubMed
Koo 1996 {published data only}
-
- Koo J, Gambla C. Psychopharmacology for dermatologic patients. Dermatologic Clinics 1996;14(3):509‐23. - PubMed
Krumholz 1970 {published data only}
-
- Krumholz. Pimozide versus standards versus placebo. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1970;7(2):68‐70.
Lapierre 1976 {published data only}
-
- Lapierre YD, Lavallee J. A controlled pimozide, fluphenazine and group psychotherapy study of chronic schizophrenics. Psychiatric Journal of the University of Ottawa 1976;1:8‐13.
-
- Lapierre YD, Lavallee J. Pimozide and the social behavior of schizophrenics. Current Therapeutic Research 1975;18(1):181‐8. - PubMed
Lehmann 1970 {published data only}
-
- Lehmann B. Pimozide versus fluphenazine. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1970;7(2):61‐3.
Mahal 1975 {published data only}
-
- Mahal AS, Janakiramaiah N. A double blind placebo controlled trial of pimozide (R6238) on 49 hospitalized chronic schizophrenics. Indian Journal of Psychiatry 1975;17(1):45‐55.
Marshall 1971 {published data only}
-
- Marshall WK. Pimozide (Orap): a multicentre study. Clinical Trials Journal 1971;7(Suppl 2):49‐54.
Masiak 1976 {published data only}
-
- Masiak M, Majczak A, Hascewicz‐Rzecka M. Pimozide and piportil in the treatment of chronic schizophrenia (preliminary communication) [Badania nad zastosowaniem pimozidu i piportilu w leczeniu chorych na przewlekla schizofrenie]. Psychiatrica Poland 1976;10(6):655‐60. - PubMed
McCoy 1992 {published data only}
-
- McCoy LM, Schwazkopf SB, Martin D. Rapid response to pimozide in treatment resistant delusional disorder. Annals of Clinical Psychiatry 1992;4(2):95‐8.
McCreadie 1978 {published data only}
-
- McCreadie RG, Main CJ, Dunlop RA. Token economy, pimozide and chronic schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 1978;133:179‐81. - PubMed
McCreadie 1983 {published data only}
-
- McCreadie RG, McKane JP, Mackie M. Weekly pimozide versus fluphenazine decanoate in schizophrenic out‐ and day‐patients. British Journal of Psychiatry 1983;143:97‐8. - PubMed
Meltzer 1986 {published data only}
-
- Meltzer HY. Novel approaches to the pharmacotherapy of schizophrenia. Drug Development Research 1986;9:23‐40.
Moller 1994 {published data only}
-
- Moller HJ, Praag HM, Aufdembrinke B, Bailey P, Barnes TRE, Beck J, et al. Negative symptoms in schizophrenia: considerations for clinical trials: working group on negative symptoms in schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 1994;115:221‐8. - PubMed
Morris 1970 {published data only}
-
- Morris P, MacKenzie D, Masheter HC. A comparative double blind trial of pimozide and fluphenazine in chronic schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 1970;117:683‐4. - PubMed
Neziroglu 1997 {published data only}
-
- Neziroglu F, Yaryura Tobias JA. A review of cognitive behavioral and pharmacological treatment of body dysmorphic disorder. Behavioral Modification 1997;21:324‐40. - PubMed
Opler 1994 {published data only}
-
- LA Opler, Albert D, Ramirez PM. Psychopharmacologic treatment of negative symptoms. Comprehensive Psychiatry 1994;35(1):16‐24. - PubMed
Opler 1995 {published data only}
-
- Opler LA, Klahr DM, Ramirez PM. Pharmacologic treatment of delusions. Psychiatr Clin North Am 1995;18(2):379‐91. - PubMed
Phillips 1996 {published data only}
-
- Phillips KA. Pharmacologic treatment of body dysmorphic disorder. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1996;32(4):597‐605. - PubMed
Pinals 1996 {published data only}
-
- Pinals DA, Malhotra AK, Missar CD, Pickar D, Breier A. Lack of gender differences in neuroleptic response in patients with schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 1996;22:215‐22. - PubMed
Poldinger 1976 {published data only}
-
- Poldinger W. Application of the neuroleptic pimozide (ORAP‐R6238) for tranquillizer indications in a controlled study. International Pharmacopsychiatry 1976;11:16‐24. - PubMed
Reyntjens 1972 {published data only}
-
- Reyntjens AM, Mierlo FP. A comative double‐blind trial of pimozide in stress‐induced psychic and functional disorders. Current Medical Research Opinion 1972;1:116‐22. - PubMed
Ruiz 1975 {published data only}
-
- Ruiz Ruiz M, Miro Quintana L, Sentis Vilalta J. A clinical study with pimozide in chronic schizophrenics [Estudio clinico con pimocide en las esquizophrenias de evolucion cronica]. Revista de Psiquiatria y Psicologia Medica de Europa y America Latinas 1975;12(4):247‐56. [PsycINFO 65‐08563]
Sims 1975 {published data only}
-
- Sims AC, Burnside IG. Activity in chronic schizophrenic patients: comparison of pimozide with fluphenazine in a double blind trial. Psychological Medicine 1975;5:161‐4. - PubMed
Singh 1971 {published data only}
-
- Singh AN. Evaluation of clinical efficacy of pimozide as maintenance therapy in chronic schizophrenic patients. Current Therapeutic Research 1971;13(11):695‐705. - PubMed
Smythies 1974 {published data only}
-
- Smythies JR, Beaton JM. A pilot study of pimozide in schizophrenia. Journal of Psychiatric Research 1974;11:71‐2. - PubMed
Srinivasan 1994 {published data only}
-
- Srinivasan TN, Sureshi TR, Jayaram V, Fernandez MP. Nature and treatment of delusional parasitosis: a different experience in India. International Journal of Dermatology 1994;33(12):851‐5. - PubMed
Sterkmans 1968 {published data only}
-
- Sterkmans P, Brugmans J, Gevers F. The clinical efficacy of pimozide in chronic psychotic patients. Clinical Trials Journal 1968;5(4):1107‐12.
Sugerman 1971 {published data only}
-
- Sugerman AA. A pilot study of pimozide in chronic schizophrenic patients. Current Therapeutic Research 1971;13(11):706‐13. - PubMed
Svestka 1972 {published data only}
-
- Svestka J, Nahunek K. A comparison of pimozide with perphenazine in the treatment of acute schizophrenic psychoses. Activitas Nervosa Superior 1972;14:93‐4. - PubMed
Tegeler 1983 {published data only}
-
- Tegeler J, Woller W. Therapeutische manahmen bei spaten extrapyramidalen hyperkineson. Fortschr Neurology Psychiatry 1983;51:203‐26. - PubMed
Tueth 1983 {published data only}
-
- Teuth MJ, Cheong JA. Clinical uses of pimozide. Southern Medical Journal 1993;86(3):344‐9. - PubMed
Ungvari 1986 {published data only}
-
- Ungvari G, Vladar K. Pimozide treatment for delusion of infestation. Acta Nervosa Superior Praha 1986;28:103‐7. - PubMed
Vanelle 1996 {published data only}
-
- Vanelle JM. Profile of the action of neuroleptics in deficit schizophrenia [Profil d'action des neuroleptiques dans les schizophrenies defictaires]. L'Encephale 1996;22(Suppl 2):33‐9. - PubMed
van Kammen 1982 {published data only}
-
- Kammen DP, Docherty JP, Marder SR, Schulz SC, Dalton L, Bunney WE Jr. Antipsychotic effects of pimozide in schizophrenia: treatment response prediction with acute dextroamphetamine response. Archives of General Psychiatry 1982;39:261‐6. - PubMed
van Kammen 1987 {published data only}
-
- Kammen DP, Hommer DW, Malas KL. Effect of pimozide on positive and negative symptoms in schizophrenic patients: are negative symptoms state dependent?. Neuropsychobiology 1987;18:113‐7. - PubMed
Van Wyck 1972 {published data only}
-
- Wyk AJ, Grove JJ. Pimozide: an effective, once daily oral therapy for schizophrenia. South African Medical Journal 1972;46:515‐7. - PubMed
Watt 1983 {published data only}
-
- Watt DC, Katz K, Shepherd M. The natural history of schizophrenia: a 5‐year prospective follow‐up of a representative sample of schizophrenics by means of a standardized clinical and social assessment. Psychological Medicine 1983;13:663‐70. - PubMed
Welbel 1979 {published data only}
-
- Welbel L. Differences in the clinical effects of various neuroleptics. Psychiatrica Poland 1980;XIV(2):113‐8. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Umene 1972 {published data only}
-
- Umene Z, Uriu K, Kurata M, Minagawa M, Nakazato T, Tachibana K, Nishimura M, Suzuki T. A double‐blind comparison of pimozide (r‐6238) with chlorpromazine in chronic schizophrenia. Rinsho Yakuri 1972;3(2):91‐102. [MEDLINE: ; PMID 2694767]
Additional references
Adams 2007
Altman 1996
Andreasen 1982
-
- Andreasen NC. Negative symptoms in schizophrenia: definition and reliability. Archives of General Psychiatry 1982;39(7):784‐8. - PubMed
Begg 1996
-
- Begg C, Cho M, Eastwood S, Horton R, Moher D, Olkin I, et al. Improving the quality of randomized controlled trials: the CONSORT statement. JAMA 1996;276:637‐9. - PubMed
Bland 1997
BNF
BNF 2012
-
- Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain. British National Formulary. Vol. 63, The Pharmaceutical Press, 2012.
Boissel 1999
-
- Boissel JP, Cucherat M, Li W, Chatellier G, Gueyffier F, Buyse M, et al. The problem of therapeutic efficacy indices. 3. Comparison of the indices and their use [Apercu sur la problematique des indices d'efficacite therapeutique, 3: comparaison des indices et utilisation. Groupe d'Etude des Indices D'efficacite]. Therapie 1999;54(4):405‐11. [PUBMED: 10667106] - PubMed
Caldwell 1992
-
- Caldwell CB, Gottesman II. Schizophrenia: a high‐risk factor for suicide: clues to risk reduction. Suicide and Life‐Threatening Behavior 1992;22:479‐93. - PubMed
Chouinard 1980
-
- Chouinard G, Ross‐Chouinard A, Annable L, Jones B. The Extrapyramidal Symptom Rating Scale. Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences 1980;7:233.
Cotton 2006
-
- Cotton S, Yuen HP, Berger G, McGorry P. Last observation carried forward in psychiatric research: a flawed gold standard?. Schizophrenia Research 2006;81(Suppl):227.
CSM 1990
-
- Committee on Safety of Medicines. Cardiotoxic effects of pimozide. Current Problems 1990;29:1‐2.
Davies 2007
-
- Davies EJ. Developmental aspects of schizophrenia and related disorders: possible implications for treatment strategies. Advances in Psychiatric Treatment 2007;13:384‐91.
De Hert 2011
Deeks 2000
-
- Deeks J. Issues in the selection for meta‐analyses of binary data. Proceedings of the 8th International Cochrane Colloquium; 2000 October 25‐28; Cape Town. Cape Town: The Cochrane Collaboration, 2000.
Divine 1992
-
- Divine GW, Brown JT, Frazier LM. The unit of analysis error in studies about physicians' patient care behavior. Journal of General Internal Medicine 1992;7(6):623‐9. - PubMed
Donner 2002
-
- Donner A, Klar N. Issues in the meta‐analysis of cluster randomized trials. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21:2971‐80. - PubMed
Egger 1997
Elbourne 2002
-
- Elbourne D, Altman DG, Higgins JPT, Curtina F, Worthingtond HV, Vaile A. Meta‐analyses involving cross‐over trials: methodological issues. International Journal of Epidemiology 2002;31(1):140‐9. - PubMed
Feighner 1972
-
- Feighner JP, Robins E, Guze SB, Woodruff RA, Winokur G, Munos R. Diagnostic criteria for the use in psychiatric research. Archives of General Psychiatry 1972;26:57‐63. - PubMed
Furukawa 2006
-
- Furukawa TA, Barbui C, Cipriani A, Brambilla P, Watanabe N. Imputing missing standard deviations in meta‐analyses can provide accurate results. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2006;59(7):7‐10. - PubMed
Gulliford 1999
-
- Gulliford MC. Components of variance and intraclass correlations for the design of community‐based surveys and intervention studies: data from the Health Survey for England 1994. American Journal of Epidemiology 1999;149:876‐83. - PubMed
Guy 1976
-
- Guy W. Early Clinical Drug Evaluation (ECDEU) Assessment Manual for Psychopharmacology. Washington, DC: National Institute of Mental Health, Publication No.76‐338, 1976.
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2005
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions 4.2.5 [updated May 2005]. Cochrane Library. Vol. 3, Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2005.
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.2 [updated September 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. www.cochrane‐handbook.org..
ICD 10 1994
-
- World Health Organisation. ICD‐10 Classification of Mental and Behavioral Disorders. London: Churchill Livingstone, 1991.
Jadad 1996
-
- Jadad A, Moore A, Carrol D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJM, Gavanagh DJ, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomised controlled trials: is blinding necessary?. Controlled Clinical Trials 1996;17:1‐12. - PubMed
Janssen 1998
-
- Janssen PA. Function and dysfunction of the basal ganglia. In: Bain TA, Healy D, Shorter E editor(s). The Rise of Psychopharmacology and the Story of CINP. Budapest: Animula Publishing House, 1998.
Jusic 1994
-
- Jusic N, Lader M. Post‐mortem antipsychotic drug concentrations and unexplained deaths. British Journal of Psychiatry 1994;165:787‐91. - PubMed
Kaplan 1994
-
- Kaplan HI, Sadock BJ, Grebb JA. Other psychotic disorders. In: Kaplan HI, Sadock BJ, Grebb JA editor(s). Synopsis of Psychiatry. London: Williams and Wilkins, 1994:487‐512.
Katz 1963
-
- Katz MM, Lyerly SB. Methods for measuring adjustment and social behaviour in the community. I. Rationale, description, discriminative validity and scale development. Psychological Reports 1963;13:503‐35.
Kay 1986
-
- Kay SR, Opler LA, Fiszbein A. Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) Manual. North Tonawanda, NY: Multi‐Health Systems, 1986.
Kay 1987
-
- Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA. The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bulletin 1987;13(2):261‐76. - PubMed
King 1995
-
- King DJ. Neuroleptics and schizophrenia. Seminars in Clinical Psychopharmacology 1995:259‐327.
Leucht 2005
-
- Leucht S, Kane JM, Kissling W, Hamann J, Etschel E, Engel RR. What does the PANSS mean?. Schizophrenia Research 2005;79(2‐3):231‐8. [PUBMED: 15982856] - PubMed
Leucht 2005a
-
- Leucht S, Kane JM, Kissling W, Hamann J, Etschel E, Engel R. Clinical implications of Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale scores. British Journal of Psychiatry 2005;187:366‐71. [PUBMED: 16199797] - PubMed
Leucht 2007
Marshall 2000
-
- Marshall M, Lockwood A, Bradley C, Adams C, Joy C, Fenton M. Unpublished rating scales: a major source of bias in randomised controlled trials of treatments for schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 2000;176:249‐52. - PubMed
Moher 1998
-
- Moher D, Pham B, Jones A, Cook DJ, Jadad AR, Moher M, et al. Does quality of reports of randomised trials affect estimates of intervention efficacy reported in meta‐analyses?. Lancet 1998;352:609‐13. - PubMed
Moher 2001
-
- Moher D, Schulz KF, Altman D. The CONSORT statement: revised recommendations for improving the quality of reports of parallel‐group randomized trials. JAMA 2001;285:1987‐91. - PubMed
Montgomery 1979
-
- Montgomery S.A, Asberg M. Montgomery Asberg Depression Rating Scale. British Journal of Psychiatry 1979;134:382‐89. - PubMed
Munro 1980
-
- Munro A. Monosymptomatic hypochondriacal psychosis. British Journal of Hospital Medicine 1980;24:34‐8. - PubMed
Opler 1991
-
- Opler LA, Feinberg SS. The role of pimozide in clinical psychiatry. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1991;52(5):221‐33. - PubMed
Overall 1962
-
- Overall JE, Gorham DR. The Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale. Psychological Reports 1962;10:799‐812.
Platt 1980
-
- Platt S, Weyman A, Hirsch S, Hewett S. The Social Behaviour Assessment Schedule (SBAS): rationale, contents, scoring and reliability of a new interview schedule. Social Psychiatry 1980;15:43‐55.
Quraishi 1999
Radhakrishnan 2012
-
- Radhakrishnan R, Butler R, Head L. Dementia in schizophrenia. Advances in Psychiatric Treatment 2012;18:144‐53.
Schneider 1983
-
- Schneider LC, Struening EL. SLOF: a behavioral rating scale for assessing the mentally ill. Social Work Research & Abstracts 1983;19(3):9‐21. - PubMed
Schulz 1994
-
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Grimes DA, Altman DG. Assessing the quality of randomization from reports of controlled trials published in obstetrics and gynecology journals. JAMA 1994;272:125‐8. - PubMed
Schulz 1995
-
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias: dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995 1995;273:408‐12. - PubMed
Schünemann 2008
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, et al. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JPT, Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Copenhagen: The Cochrane Collaboration, 2008:359‐83.
Silverstone 1995
-
- Silverstone T, Turner P. Drug Treatment in Psychiatry. 5th Edition. London: Routledge, 1995.
Simpson 1970
-
- Simpson GM, Angus JWS. A rating scale for extrapyramidal side effects. Acta Psychiatria Scandinavica Supplementum 1970;212:11‐9. - PubMed
Turner 1990
-
- Turner WM, Tsuang MT. The impact of substance abuse on the course and outcome of schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bulletin 1990;16:18. - PubMed
Udabe 1998
-
- Udabe RU. Psychopharmacology in Argentina. In: Bain TA, Healy D, Shorter E editor(s). The Rise of Psychopharmacology and the Story of CINP. Budapest: Animula Publishing House, 1998.
Ukoumunne 1999
-
- Ukoumunne OC, Gulliford MC, Chinn S, Sterne JAC, Burney PGJ. Methods for evaluating area‐wide and organistation‐based intervention in health and health care: a systematic review. Health Technology Assessment 1999;3(5):1‐75. - PubMed
Wing 1974
-
- Wing JK, Cooper J, Sartorious N. The Measurement and Classification of Symptoms. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1974.
Winokur 1977
-
- Winokur G. Delusional disorder (paranoia). Comprehensive Psychiatry 1977;18:511‐21. - PubMed
Xia 2009
-
- Xia J, Adams CE, Bhagat N, Bhagat V, Bhoopathi P, El‐Sayeh H, et al. Loss to outcomes stakeholder survey: the LOSS study. Psychiatric Bulletin 2009;33(7):254‐7.
Yaryura‐Tobias 1998
-
- Yaryura‐Tobias JA. Serotonin and obsessive compulsive disorder. In: Bain TA, Healy D, Shorter E editor(s). The Rise of Psychopharmacology and the Story of CINP. Budapest: Animula Hublishing House, 1998.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

