Cognitive, sensory, and psychosocial characteristics in patients with Bardet-Biedl syndrome
- PMID: 24194441
- PMCID: PMC4419571
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.a.36245
Cognitive, sensory, and psychosocial characteristics in patients with Bardet-Biedl syndrome
Abstract
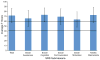
Forty-two patients with a clinical diagnosis of Bardet-Biedl syndrome ages 2-61 years were given a neuropsychological test battery to evaluate cognitive, sensory, and behavioral functioning. These tests included the Wechsler scales of intelligence, Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test, Boston Naming Test, D-KEFS Verbal Fluency Test, D-KEFS Color-Word Interference Test, D-KEFS Sorting Test, Wide Range Achievement Test: Math and Reading Subtests, Purdue Pegboard, The University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test, Social Communication Questionnaire, Social Responsiveness Scale, and Behavior Assessment System for Children, Second Edition, Parent Rating Scale. On the age appropriate Wechsler scale, the mean Verbal Comprehension was 81 (n = 36), Working Memory was 81 (n = 36), Perceptual Reasoning was 78 (n = 24) and Full Scale IQ was 75 (n = 26). Memory for a word list (Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test) was in the average range with a mean of 89 (n = 19). Fine motor speed was slow on the Purdue with mean scores 3-4 standard deviations below norms. All subjects were microsmic on the University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test. Of these 42 patients, only 6 were able to complete all auditory and visual tests; 52% were unable to complete the visual tests due to impaired vision. A wide range of behavioral issues were endorsed on questionnaires given to parents. Most had social skill deficits but no pattern of either externalizing or internalizing problems. We identify a characteristic neuro-behavioral profile in our cohort comprised of reduced IQ, impaired fine-motor function, and decreased olfaction.
Keywords: Bardet-Biedl syndrome; Intellectual disability; brain development; olfaction; psychometric testing.
© 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Interest of a new instrument to assess cognition in schizophrenia: The Brief Assessment of Cognition in Schizophrenia (BACS)].Encephale. 2008 Dec;34(6):557-62. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2007.12.005. Epub 2008 Jul 9. Encephale. 2008. PMID: 19081451 French.
-
Cognitive development in children with new-onset Rolandic epilepsy and Rolandic discharges without seizures: Focusing on intelligence, visual perception, working memory and the role of parents' education.Epilepsy Behav. 2024 Mar;152:109596. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2023.109596. Epub 2024 Feb 12. Epilepsy Behav. 2024. PMID: 38350362
-
Panayiotopoulos syndrome and Gastaut syndrome are distinct entities in terms of neuropsychological findings.Epilepsy Behav. 2019 Oct;99:106447. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2019.106447. Epub 2019 Aug 6. Epilepsy Behav. 2019. PMID: 31398558 Clinical Trial.
-
Neuropsychological function in Tourette syndrome.Adv Neurol. 2001;85:103-11. Adv Neurol. 2001. PMID: 11530420 Review.
-
Cognitive characteristics of children with genetic syndromes.Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2007 Jul;16(3):599-616. doi: 10.1016/j.chc.2007.03.002. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2007. PMID: 17562581 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
DNA Methylation Signature of a Lifestyle-based Resilience Index for Cognitive Health.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 27:rs.3.rs-5423573. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5423573/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025 Apr 22;17(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s13195-025-01733-7. PMID: 39649166 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Collaborative effort: managing Bardet-Biedl syndrome in pediatric patients. Case series and a literature review.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 18;15:1424819. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1424819. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39092285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Potential Contributory Role for Ciliary Dysfunction in the 16p11.2 600 kb BP4-BP5 Pathology.Am J Hum Genet. 2015 May 7;96(5):784-96. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2015.04.002. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Am J Hum Genet. 2015. PMID: 25937446 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome-guided GLP-1 receptor therapy rescues metabolic and behavioral disruptions in a Bardet-Biedl syndrome mouse model.J Clin Invest. 2025 Apr 15;135(12):e184636. doi: 10.1172/JCI184636. eCollection 2025 Jun 16. J Clin Invest. 2025. PMID: 40233116 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Signaling by primary cilia in development and disease.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Mar 21;11:1186367. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1186367. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37025179 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ansley SJ, Badano JL, Blacque OE, Hill J, Hoskins BE, Leitch CC, Kim JC, Ross AJ, Eichers ER, Teslovich TM, Mah AK, Johnsen RC, Cavender JC, Lewis RA, Leroux MR, Beales PL, Katsanis N. Basal body dysfunction is a likely cause of pleiotropic Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Nature. 2003;425:628–633. - PubMed
-
- Baker K, Northam GB, Chong WK, Banks T, Beales P, Baldeweg T. Neocortical and hippocampal volume loss in a human ciliopathy: A quantitative MRI study in Bardet–Biedl syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2011;155:1–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

