High-Resolution MR Imaging of the Human Brainstem In vivo at 7 Tesla
- PMID: 24194710
- PMCID: PMC3810670
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2013.00710
High-Resolution MR Imaging of the Human Brainstem In vivo at 7 Tesla
Abstract
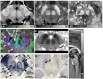
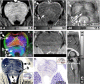
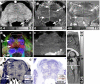
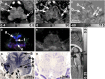
The human brainstem, which comprises a multitude of axonal nerve fibers and nuclei, plays an important functional role in the human brain. Depicting its anatomy non-invasively with high spatial resolution may thus in turn help to better relate normal and pathological anatomical variations to medical conditions as well as neurological and peripheral functions. We explored the potential of high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at 7 T for depicting the intricate anatomy of the human brainstem in vivo by acquiring and generating images with multiple contrasts: T 2-weighted images, quantitative maps of longitudinal relaxation rate (R 1 maps) and effective transverse relaxation rate ([Formula: see text] maps), magnetic susceptibility maps, and direction-encoded track-density images. Images and quantitative maps were compared with histological stains and anatomical atlases to identify nerve nuclei and nerve fibers. Among the investigated contrasts, susceptibility maps displayed the largest number of brainstem structures. Contrary to R 1 maps and T 2-weighted images, which showed rather homogeneous contrast, [Formula: see text] maps, magnetic susceptibility maps, and track-density images clearly displayed a multitude of smaller and larger fiber bundles. Several brainstem nuclei were identifiable in sections covering the pons and medulla oblongata, including the spinal trigeminal nucleus and the reticulotegmental nucleus on magnetic susceptibility maps as well as the inferior olive on R 1, [Formula: see text], and susceptibility maps. The substantia nigra and red nuclei were visible in all contrasts. In conclusion, high-resolution, multi-contrast MR imaging at 7 T is a versatile tool to non-invasively assess the individual anatomy and tissue composition of the human brainstem.
Keywords: anatomy; brain; brainstem; diffusion tensor imaging; effective transverse relaxation; longitudinal relaxation; quantitative susceptibility mapping; track-density imaging.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Brainstem anatomy with 7-T MRI: in vivo assessment and ex vivo comparison.Eur Radiol Exp. 2023 Nov 16;7(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s41747-023-00389-y. Eur Radiol Exp. 2023. PMID: 37968363 Free PMC article.
-
Track-Density Imaging of the Human Brainstem for Anatomic Localization of Fiber Tracts and Nerve Nuclei in Vivo: Initial Experience with 3-T Magnetic Resonance Imaging.World Neurosurg. 2016 Sep;93:286-92. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2016.05.085. Epub 2016 Jun 4. World Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 27269211
-
Mapping the human brainstem: Brain nuclei and fiber tracts at 3 T and 7 T.NMR Biomed. 2019 Sep;32(9):e4118. doi: 10.1002/nbm.4118. Epub 2019 Jul 9. NMR Biomed. 2019. PMID: 31286600
-
Structural and Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Cerebellum: Considerations for Assessing Cerebellar Ataxias.Cerebellum. 2016 Feb;15(1):21-25. doi: 10.1007/s12311-015-0738-9. Cerebellum. 2016. PMID: 26521073 Review.
-
Anatomy of the brainstem: a gaze into the stem of life.Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2010 Jun;31(3):196-219. doi: 10.1053/j.sult.2010.03.006. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2010. PMID: 20483389 Review.
Cited by
-
A Topographic Atlas of the Human Brainstem in the Ponto-Mesencephalic Junction Plane.Front Neuroanat. 2021 Aug 13;15:627656. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2021.627656. eCollection 2021. Front Neuroanat. 2021. PMID: 34483849 Free PMC article.
-
Visualizing the Human Subcortex Using Ultra-high Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging.Brain Topogr. 2018 Jul;31(4):513-545. doi: 10.1007/s10548-018-0638-7. Epub 2018 Mar 2. Brain Topogr. 2018. PMID: 29497874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brainstem anatomy with 7-T MRI: in vivo assessment and ex vivo comparison.Eur Radiol Exp. 2023 Nov 16;7(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s41747-023-00389-y. Eur Radiol Exp. 2023. PMID: 37968363 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo Brainstem Imaging in Alzheimer's Disease: Potential for Biomarker Development.Front Aging Neurosci. 2018 Sep 11;10:266. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00266. eCollection 2018. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30254583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiparametric MRI for Characterization of the Basal Ganglia and the Midbrain.Front Neurosci. 2021 Jun 21;15:661504. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.661504. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34234639 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bergman R. A., Afifi A. K., Heidger P. M. (eds). (1989). “Atlas of microscopic anatomy: companion to histology and neuroanatomy,” in Central Nervous System, 2nd Edn (Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders Company; ), 418–495
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

