Plasma microRNA panel for minimally invasive detection of breast cancer
- PMID: 24194846
- PMCID: PMC3806790
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076729
Plasma microRNA panel for minimally invasive detection of breast cancer
Abstract
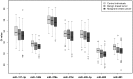
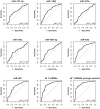
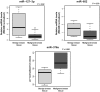
Over the last few years, circulating microRNAs (miRNAs) have emerged as promising novel and minimally invasive markers for various diseases, including cancer. We already showed that certain miRNAs are deregulated in the plasma of breast cancer patients when compared to healthy women. Herein we have further explored their potential to serve as breast cancer early detection markers in blood plasma. Circulating miR-127-3p, miR-376a and miR-652, selected as candidates from a miRNA array-based screening, were found to be associated with breast cancer for the first time (n = 417). Further we validated our previously reported circulating miRNAs (miR-148b, miR-376c, miR-409-3p and miR-801) in an independent cohort (n = 210) as elevated in the plasma of breast cancer patients compared to healthy women. We described, for the first time in breast cancer, an over-representation of deregulated miRNAs (miR-127-3p, miR-376a, miR-376c and miR-409-3p) originating from the chromosome 14q32 region. The inclusion of patients with benign breast tumors enabled the observation that miR-148b, miR-652 and miR-801 levels are even elevated in the plasma of women with benign tumors when compared to healthy controls. Furthermore, an analysis of samples stratified by cancer stage demonstrated that miR-127-3p, miR-148b, miR-409-3p, miR-652 and miR-801 can detect also stage I or stage II breast cancer thus making them attractive candidates for early detection. Finally, ROC curve analysis showed that a panel of these seven circulating miRNAs has substantial diagnostic potential with an AUC of 0.81 for the detection of benign and malignant breast tumors, which further increased to 0.86 in younger women (up to 50 years of age).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Circulating microRNAs in plasma as early detection markers for breast cancer.Int J Cancer. 2013 Apr 1;132(7):1602-12. doi: 10.1002/ijc.27799. Epub 2012 Sep 14. Int J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 22927033
-
Plasma microRNAs as potential new biomarkers for early detection of early gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Apr 7;25(13):1580-1591. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i13.1580. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30983818 Free PMC article.
-
Novel circulating microRNA signature as a potential non-invasive multi-marker test in ER-positive early-stage breast cancer: a case control study.Mol Oncol. 2014 Jul;8(5):874-83. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2014.03.002. Epub 2014 Mar 16. Mol Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24694649 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers in hepatocellular carcinoma screening: a validation set from China.Medicine (Baltimore). 2015 Mar;94(10):e603. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000603. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015. PMID: 25761179 Free PMC article.
-
The role and diagnostic value of deregulated miRNAs in cervical cancer.Discov Oncol. 2025 May 25;16(1):922. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02744-4. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40413660 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of miR-652-3p and Effect on Apoptosis and Drug Sensitivity in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Jun 5;2018:5724686. doi: 10.1155/2018/5724686. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29967774 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-652 induces NED in LNCaP and EMT in PC3 prostate cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2018 Apr 10;9(27):19159-19176. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24937. eCollection 2018 Apr 10. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29721191 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-free circulating DNA integrity is an independent predictor of impending breast cancer recurrence.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 24;8(33):54537-54547. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17384. eCollection 2017 Aug 15. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28903362 Free PMC article.
-
Phenylpropanoids for the control of fungal diseases of postharvest fruit.Plant Mol Biol. 2025 Feb 28;115(2):39. doi: 10.1007/s11103-025-01568-8. Plant Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40021523 Review.
-
Early second-trimester serum microRNAs as potential biomarker for nondiabetic macrosomia.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:394125. doi: 10.1155/2014/394125. Epub 2014 Oct 27. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25405200 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F (2011) Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, et al (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61: 69–90. - PubMed
-
- Howlader N NA, Krapcho M, Neyman N, Aminou R, Waldron W, et al.. (2011) SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2008. National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD: http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2008/. (Accessed on November 7, 2011)
-
- Bleyer A, Welch HG (2012) Effect of three decades of screening mammography on breast-cancer incidence. N Engl J Med 367: 1998–2005. - PubMed
-
- Nystrom L, Andersson I, Bjurstam N, Frisell J, Nordenskjold B, et al. (2002) Long-term effects of mammography screening: updated overview of the Swedish randomised trials. Lancet 359: 909–919. - PubMed
-
- Checka CM, Chun JE, Schnabel FR, Lee J, Toth H (2012) The relationship of mammographic density and age: implications for breast cancer screening. AJR Am J Roentgenol 198: W292–295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

