Transgenic rabbits that overexpress the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) generate higher quantities and improved qualities of anti-thymocyte globulin (ATG)
- PMID: 24194847
- PMCID: PMC3806768
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076839
Transgenic rabbits that overexpress the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) generate higher quantities and improved qualities of anti-thymocyte globulin (ATG)
Abstract
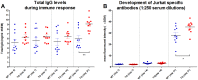
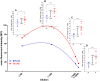
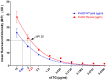
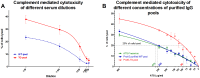
Immune suppression with rabbit anti-thymocyte globulin (rATG) is a well-established therapeutic concept for preventing host rejection of transplanted organs and graft versus host disease. Increasing the efficiency of rATG production by reducing the number of animals would be highly beneficial to lower cost and to improve quality standards. We have developed transgenic (Tg) mice and rabbits that overexpress the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) and have shown an augmented humoral immune response in these animals. To test whether our FcRn Tg rabbits produced rATG more efficiently, we immunized them and their New Zealand White controls with live Jurkat cells. By day 21 after immunization, Tg animals produced significantly, 1.5 times higher amount of total IgG compared to their wt littermates. Also, the binding efficiency of Tg sera to Jurkat cells and their complement-mediated cytotoxicity was significantly higher. The purified Tg IgG preparation contained 2.6 the amount of Jurkat specific IgG as the wt preparation analyzed by complement-mediated lysis, suggesting greater antigen-specific B cell activation in the Tg rabbits. To test this hypothesis, immunization with ovalbumin and human α1-antitrypsin was performed, resulting in significantly greater numbers of antigen-specific B-cells in the FcRn Tg rabbits as compared with wt controls. The shift towards significantly larger populations of antigen-specific B cells relative to the non-specific B cell pool is further corroborated by our previous findings in FcRn Tg mice. Consequently, our FcRn Tg rabbits have the potential to offer substantial qualitative and quantitative improvements for the production of rATG and other polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
FcRn Overexpression Expands Diversity of the Humoral Immune Response in bFcRn Transgenic Mice.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 21;11:1887. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01887. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32973781 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the rabbit neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) and analyzing the immunophenotype of the transgenic rabbits that overexpresses FcRn.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e28869. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028869. Epub 2012 Jan 11. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22247762 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerating antibody discovery using transgenic animals overexpressing the neonatal Fc receptor as a result of augmented humoral immunity.Immunol Rev. 2015 Nov;268(1):269-87. doi: 10.1111/imr.12364. Immunol Rev. 2015. PMID: 26497527 Review.
-
Transgenic expression of bovine neonatal Fc receptor in mice boosts immune response and improves hybridoma production efficiency without any sign of autoimmunity.Immunol Lett. 2011 Jun 30;137(1-2):62-9. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2011.02.018. Epub 2011 Feb 19. Immunol Lett. 2011. PMID: 21338624
-
Recent advances using FcRn overexpression in transgenic animals to overcome impediments of standard antibody technologies to improve the generation of specific antibodies.MAbs. 2011 Sep-Oct;3(5):431-9. doi: 10.4161/mabs.3.5.17023. Epub 2011 Sep 1. MAbs. 2011. PMID: 22048692 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Overexpression of Bovine FcRn in Mice Enhances T-Dependent Immune Responses by Amplifying T Helper Cell Frequency and Germinal Center Enlargement in the Spleen.Front Immunol. 2015 Jul 20;6:357. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00357. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26257730 Free PMC article.
-
The neonatal Fc receptor: Key to homeostasic control of IgG and IgG-related biopharmaceuticals.Am J Transplant. 2019 Jul;19(7):1881-1887. doi: 10.1111/ajt.15366. Epub 2019 Apr 15. Am J Transplant. 2019. PMID: 30903736 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Foxo1-Inducible Transcriptional Repressor Zfp125 Causes Hepatic Steatosis and Hypercholesterolemia.Cell Rep. 2018 Jan 9;22(2):523-534. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.12.053. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 29320745 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-specific STORM super-resolution imaging reveals nanoscale organization of cannabinoid signaling.Nat Neurosci. 2015 Jan;18(1):75-86. doi: 10.1038/nn.3892. Epub 2014 Dec 8. Nat Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25485758 Free PMC article.
-
FcRn Overexpression Expands Diversity of the Humoral Immune Response in bFcRn Transgenic Mice.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 21;11:1887. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01887. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32973781 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mohty M (2007) Mechanisms of action of antithymocyte globulin: T-cell depletion and beyond. Leukemia : official journal of the Leukemia Society of America, Leukemia Research Fund, UK 21: 1387–1394. - PubMed
-
- Marsh J, Schrezenmeier H, Marin P, Ilhan O, Ljungman P, et al. (1999) Prospective randomized multicenter study comparing cyclosporin alone versus the combination of antithymocyte globulin and cyclosporin for treatment of patients with nonsevere aplastic anemia: a report from the European Blood and Marrow Transplant (EBMT) Severe Aplastic Anaemia Working Party. Blood 93: 2191–2195. - PubMed
-
- Aversa F, Tabilio A, Velardi A, Cunningham I, Terenzi A, et al. (1998) Treatment of high-risk acute leukemia with T-cell-depleted stem cells from related donors with one fully mismatched HLA haplotype. N Engl J Med 339: 1186–1193. - PubMed
-
- Ringden O, Remberger M, Carlens S, Hagglund H, Mattsson J, et al. (1998) Low incidence of acute graft-versus-host disease, using unrelated HLA-A-, HLA-B-, and HLA-DR-compatible donors and conditioning, including anti-T-cell antibodies. Transplantation 66: 620–625. - PubMed
-
- Deeg HJ, Loughran TP Jr, Storb R, Kennedy MS, Sullivan KM, et al. (1985) Treatment of human acute graft-versus-host disease with antithymocyte globulin and cyclosporine with or without methylprednisolone. Transplantation 40: 162–166. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

