Acute treatment with docosahexaenoic acid complexed to albumin reduces injury after a permanent focal cerebral ischemia in rats
- PMID: 24194876
- PMCID: PMC3806755
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077237
Acute treatment with docosahexaenoic acid complexed to albumin reduces injury after a permanent focal cerebral ischemia in rats
Abstract
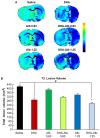
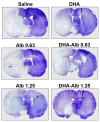
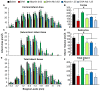
Docosahexaenoic acid complexed to albumin (DHA-Alb) is highly neuroprotective after temporary middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAo), but whether a similar effect occurs in permanent MCAo is unknown. Male Sprague-Dawley rats (270-330 g) underwent permanent MCAo. Neurological function was evaluated on days 1, 2 and 3 after MCAo. We studied six groups: DHA (5 mg/kg), Alb (0.63 or 1.25 g/kg), DHA-Alb (5 mg/kg+0.63 g/kg or 5 mg/kg+1.25 g/kg) or saline. Treatment was administered i.v. at 3 h after onset of stroke (n = 7-10 per group). Ex vivo imaging of brains and histopathology were conducted on day 3. Saline- and Alb-treated rats developed severe neurological deficits but were not significantly different from one another. In contrast, rats treated with low and moderate doses of DHA-Alb showed improved neurological score compared to corresponding Alb groups on days 2 and 3. Total, cortical and subcortical lesion volumes computed from T2 weighted images were reduced following a moderate dose of DHA-Alb (1.25 g/kg) by 25%, 22%, 34%, respectively, compared to the Alb group. The total corrected, cortical and subcortical infarct volumes were reduced by low (by 36-40%) and moderate doses (by 34-42%) of DHA-Alb treatment compared to the Alb groups. In conclusion, DHA-Alb therapy is highly neuroprotective in permanent MCAo in rats. This treatment can provide the basis for future therapeutics for patients suffering from ischemic stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Docosahexaenoic acid complexed to albumin provides neuroprotection after experimental stroke in aged rats.Neurobiol Dis. 2014 Feb;62:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2013.09.008. Epub 2013 Sep 21. Neurobiol Dis. 2014. PMID: 24063996 Free PMC article.
-
Docosahexaenoic acid complexed to human albumin in experimental stroke: neuroprotective efficacy with a wide therapeutic window.Exp Transl Stroke Med. 2012 Sep 14;4(1):19. doi: 10.1186/2040-7378-4-19. Exp Transl Stroke Med. 2012. PMID: 22980673 Free PMC article.
-
Robust docosahexaenoic acid-mediated neuroprotection in a rat model of transient, focal cerebral ischemia.Stroke. 2009 Sep;40(9):3121-6. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.555979. Epub 2009 Jun 18. Stroke. 2009. PMID: 19542051 Free PMC article.
-
Docosahexaenoic acid confers enduring neuroprotection in experimental stroke.J Neurol Sci. 2014 Mar 15;338(1-2):135-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2013.12.033. Epub 2013 Dec 31. J Neurol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24433927 Free PMC article.
-
Novel aspirin-triggered neuroprotectin D1 attenuates cerebral ischemic injury after experimental stroke.Exp Neurol. 2012 Jul;236(1):122-30. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.04.007. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Exp Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22542947 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Diabetes-induced abnormalities of mitochondrial function in rat brain cortex: the effect of n-3 fatty acid diet.Mol Cell Biochem. 2017 Nov;435(1-2):109-131. doi: 10.1007/s11010-017-3061-6. Epub 2017 May 19. Mol Cell Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28526935
-
Diabetic Stroke Severity: Epigenetic Remodeling and Neuronal, Glial, and Vascular Dysfunction.Diabetes. 2015 Dec;64(12):4260-71. doi: 10.2337/db15-0422. Epub 2015 Oct 15. Diabetes. 2015. PMID: 26470785 Free PMC article.
-
Enriched Endogenous Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Protect Cortical Neurons from Experimental Ischemic Injury.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Nov;53(9):6482-6488. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9554-y. Epub 2015 Nov 26. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26611833
-
Role of Antioxidants in Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury: New Therapeutic Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jan 28;18(2):265. doi: 10.3390/ijms18020265. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28134843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
JLX001 Modulated the Inflammatory Reaction and Oxidative Stress in pMCAO Rats via Inhibiting the TLR2/4-NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Neurochem Res. 2019 Aug;44(8):1924-1938. doi: 10.1007/s11064-019-02826-0. Epub 2019 Jun 15. Neurochem Res. 2019. PMID: 31203481
References
-
- Belayev L, Liu Y, Zhao W, Busto R, Ginsberg MD (2001) Human albumin therapy of acute ischemic stroke: Marked neuroprotective efficacy at moderate doses and with a broad therapeutic window. Stroke 32: 553–560. - PubMed
-
- Belayev L, Busto R, Zhao W, Clemens JA, Ginsberg MD (1997) Effect of delayed albumin hemodilution on infarction volume and brain edema after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. J Neuros 87: 595–601. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

