Streptococcus pneumoniae invades erythrocytes and utilizes them to evade human innate immunity
- PMID: 24194877
- PMCID: PMC3806730
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077282
Streptococcus pneumoniae invades erythrocytes and utilizes them to evade human innate immunity
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2014;9(1). doi:10.1371/annotation/de14e562-d899-48da-b677-ca61cca2cf5b
Abstract
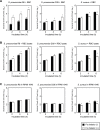
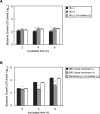
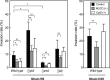
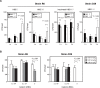
Streptococcus pneumoniae, a Gram-positive bacterium, is a major cause of invasive infection-related diseases such as pneumonia and sepsis. In blood, erythrocytes are considered to be an important factor for bacterial growth, as they contain abundant nutrients. However, the relationship between S. pneumoniae and erythrocytes remains unclear. We analyzed interactions between S. pneumoniae and erythrocytes, and found that iron ion present in human erythrocytes supported the growth of Staphylococcus aureus, another major Gram-positive sepsis pathogen, while it partially inhibited pneumococcal growth by generating free radicals. S. pneumoniae cells incubated with human erythrocytes or blood were subjected to scanning electron and confocal fluorescence microscopic analyses, which showed that the bacterial cells adhered to and invaded human erythrocytes. In addition, S. pneumoniae cells were found associated with human erythrocytes in cultures of blood from patients with an invasive pneumococcal infection. Erythrocyte invasion assays indicated that LPXTG motif-containing pneumococcal proteins, erythrocyte lipid rafts, and erythrocyte actin remodeling are all involved in the invasion mechanism. In a neutrophil killing assay, the viability of S. pneumoniae co-incubated with erythrocytes was higher than that without erythrocytes. Also, H2O2 killing of S. pneumoniae was nearly completely ineffective in the presence of erythrocytes. These results indicate that even when S. pneumoniae organisms are partially killed by iron ion-induced free radicals, they can still invade erythrocytes. Furthermore, in the presence of erythrocytes, S. pneumoniae can more effectively evade antibiotics, neutrophil phagocytosis, and H2O2 killing.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- van der Poll T, Opal SM (2009) Pathogenesis, treatment, and prevention of pneumococcal pneumonia. Lancet 374: 1543–1556. - PubMed
-
- O’Brien KL, Wolfson LJ, Watt JP, Henkle E, Deloria-Knoll M, et al. (2009) Burden of disease caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae in children younger than 5 years: global estimates. Lancet 374: 893–902. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell AM, Mitchell TJ (2010) Streptococcus pneumoniae: virulence factors and variation. Clin Microbiol Infect 16: 411–418. - PubMed
-
- Kyaw MH, Lynfield R, Schaffner W, Craig AS, Hadler J, et al. (2006) Effect of introduction of the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on drug-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae . N Engl J Med 354: 1455–1463. - PubMed
-
- Farrell DJ, Klugman KP, Pichichero M (2007) Increased antimicrobial resistance among nonvaccine serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae in the pediatric population after the introduction of 7-valent pneumococcal vaccine in the United States. Pediatr Infect Dis J 26: 123–128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

