Characterization of polymeric microneedle arrays for transdermal drug delivery
- PMID: 24194879
- PMCID: PMC3806750
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077289
Characterization of polymeric microneedle arrays for transdermal drug delivery
Abstract
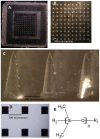
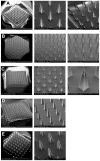
Microfabrication of dissolvable, swellable, and biodegradable polymeric microneedle arrays (MNs) were extensively investigated based in a nano sensitive fabrication style known as micromilling that is then combined with conventional micromolding technique. The aim of this study was to describe the polymer selection, and optimize formulation compounding parameters for various polymeric MNs. Inverse replication of micromilled master MNs reproduced with polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), where solid out of plane polymeric MNs were subsequently assembled, and physicochemically characterized. Dissolvable, swellable, and biodegradable MNs were constructed to depth of less than 1 mm with an aspect ratio of 3.6, and 1/2 mm of both inter needle tip and base spacing. Micromolding step also enabled to replicate the MNs very precisely and accurate. Polymeric microneedles (MN) precision was ranging from ± 0.18 to ± 1.82% for microneedle height, ± 0.45 to ± 1.42% for base diameter, and ± 0.22 to ± 0.95% for interbase spacing. Although dissolvable sodium alginate MN showed less physical robustness than biodegradable polylactic-co-glycolic acid MN, their thermogravimetric analysis is of promise for constructing these polymeric types of matrix devices.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Fabrication of polymer microneedles using a two-photon polymerization and micromolding process.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2009 Mar 1;3(2):304-11. doi: 10.1177/193229680900300211. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2009. PMID: 20144361 Free PMC article.
-
Biodegradable polymeric insulin microneedles - a design and materials perspective review.Drug Deliv. 2024 Dec;31(1):2296350. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2023.2296350. Epub 2023 Dec 26. Drug Deliv. 2024. PMID: 38147499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel method for monolithic fabrication of polymer microneedles on a platform for transdermal drug delivery.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2013;2013:156-9. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2013.6609461. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2013. PMID: 24109648
-
Fabrication of biodegradable composite microneedles based on calcium sulfate and gelatin for transdermal delivery of insulin.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017 Feb 1;71:725-734. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2016.10.063. Epub 2016 Oct 26. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017. PMID: 27987766
-
Two-photon polymerization of microneedles for transdermal drug delivery.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2010 Apr;7(4):513-33. doi: 10.1517/17425241003628171. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2010. PMID: 20205601 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanical Characterization of Dissolving Microneedles: Factors Affecting Physical Strength of Needles.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jan 30;16(2):200. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16020200. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38399254 Free PMC article.
-
Biodegradable Gelatin Methacryloyl Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Delivery.Adv Healthc Mater. 2019 Feb;8(3):e1801054. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201801054. Epub 2018 Dec 19. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019. PMID: 30565887 Free PMC article.
-
Metallic Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Delivery: Applications, Fabrication Techniques and the Effect of Geometrical Characteristics.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Dec 23;10(1):24. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10010024. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36671595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systematic review of carbohydrate-based microneedles: current status and future prospects.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2021 Jul 31;32(8):89. doi: 10.1007/s10856-021-06559-x. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2021. PMID: 34331594 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication and Evaluation of Transdermal Microneedles for a Recombinant Human Keratinocyte Growth Factor.Turk J Pharm Sci. 2021 Feb 25;18(1):96-103. doi: 10.4274/tjps.galenos.2020.21033. Turk J Pharm Sci. 2021. PMID: 33634684 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Donnelly RF, Singh TR, Morrow DI, Woolfson AD (2012a) Microneedle-mediated invasive transdermal and intradermal drug delivery. Johns Wiley & Sons, Ltd., West Sussex, UK.
-
- Kulkarni VS (2010) Microneedles-minimally invasive transdermal delivery technology, in: Kaushik D, Kilfoyle B, Thakur R, Michniak-Kohn BB (Eds.), Handbook of Non-Invasive Drug Delivery Systems. Elsevier Inc., MA, USA, 135–164.
-
- Birchall J, Coulman S, Pearton M, Allender C, Brain K, et al. (2005) Cutaneous DNA delivery and gene expression in ex vivo human skin explants via wet-etch micro fabricated micro-needles. J Drug Target 13: 415–421. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

