Characterization of polymeric microneedle arrays for transdermal drug delivery
- PMID: 24194879
- PMCID: PMC3806750
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077289
Characterization of polymeric microneedle arrays for transdermal drug delivery
Abstract
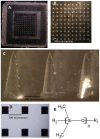
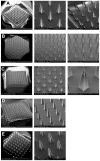
Microfabrication of dissolvable, swellable, and biodegradable polymeric microneedle arrays (MNs) were extensively investigated based in a nano sensitive fabrication style known as micromilling that is then combined with conventional micromolding technique. The aim of this study was to describe the polymer selection, and optimize formulation compounding parameters for various polymeric MNs. Inverse replication of micromilled master MNs reproduced with polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), where solid out of plane polymeric MNs were subsequently assembled, and physicochemically characterized. Dissolvable, swellable, and biodegradable MNs were constructed to depth of less than 1 mm with an aspect ratio of 3.6, and 1/2 mm of both inter needle tip and base spacing. Micromolding step also enabled to replicate the MNs very precisely and accurate. Polymeric microneedles (MN) precision was ranging from ± 0.18 to ± 1.82% for microneedle height, ± 0.45 to ± 1.42% for base diameter, and ± 0.22 to ± 0.95% for interbase spacing. Although dissolvable sodium alginate MN showed less physical robustness than biodegradable polylactic-co-glycolic acid MN, their thermogravimetric analysis is of promise for constructing these polymeric types of matrix devices.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Donnelly RF, Singh TR, Morrow DI, Woolfson AD (2012a) Microneedle-mediated invasive transdermal and intradermal drug delivery. Johns Wiley & Sons, Ltd., West Sussex, UK.
-
- Kulkarni VS (2010) Microneedles-minimally invasive transdermal delivery technology, in: Kaushik D, Kilfoyle B, Thakur R, Michniak-Kohn BB (Eds.), Handbook of Non-Invasive Drug Delivery Systems. Elsevier Inc., MA, USA, 135–164.
-
- Birchall J, Coulman S, Pearton M, Allender C, Brain K, et al. (2005) Cutaneous DNA delivery and gene expression in ex vivo human skin explants via wet-etch micro fabricated micro-needles. J Drug Target 13: 415–421. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

