High-level expression of Bacillus naganoensis pullulanase from recombinant Escherichia coli with auto-induction: effect of lac operator
- PMID: 24194930
- PMCID: PMC3806784
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078416
High-level expression of Bacillus naganoensis pullulanase from recombinant Escherichia coli with auto-induction: effect of lac operator
Abstract
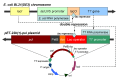
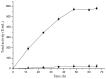
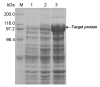
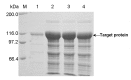
Pullulanase plays an important role in specific hydrolysis of branch points in amylopectin and is generally employed as an important enzyme in starch-processing industry. So far, however, the production level of pullulanase is still somewhat low from wide-type strains and even heterologous expression systems. Here the gene encoding Bacillus naganoensis pullulanase was amplified and cloned. For expression of the protein, two recombinant systems, Escherichia coli BL21(DE3)/pET-20b(+)-pul and E. coli BL21(DE3)/pET-22b(+)-pul, were constructed, both bearing T7 promoter and signal peptide sequence, but different in the existance of lac operator and lacI gene encoding lac repressor. Recombinant pullulanase was initially expressed with the activity of up to 14 U/mL by E. coli BL21(DE3)/pET-20b(+)-pul with IPTG induction in LB medium, but its expression level reduced continually with the extension of cryopreservation time and basal expression was observed. However, E. coli BL21(DE3)/pET-22b(+)-pul , involving lac operator downstream of T7 promoter to regulate foreign gene transcription, exhibited pullulanase activity consistently without detected basal expression. By investigating the effect of lac operator, basal expression of foreign protein was found to cause expression instability and negative effect on production of target protein. Thus double-repression strategy was proposed that lac operators in both chromosome and plasmid were bound with lac repressor to repress T7 RNA polymerase synthesis and target protein expression before induction. Consequently, the total activity of pullulanase was remarkably increased to 580 U/mL with auto-induction by lac operator-involved E. coli BL21(DE3)/pET-22b(+)-pul. When adding 0.6% glycine in culture, the extracellular production of pullulanase was significantly improved with the extracellular activity of 502 U/mL, which is a relatively higher level achieved to date for extracellular production of pullulanase. The successful expression of pullulanase with lac operator regulation provides an efficient way for enhancement of expression stability and hence high-level production of target protein in recombinant E. coli.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







Similar articles
-
[Expression and secretion regulation of Bacillus naganoensis pullulanase in recombinant Escherichia coli].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2013 Feb 4;53(2):145-53. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2013. PMID: 23627107 Chinese.
-
Soluble expression of pullulanase from Bacillus acidopullulyticus in Escherichia coli by tightly controlling basal expression.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014 Dec;41(12):1803-10. doi: 10.1007/s10295-014-1523-3. Epub 2014 Oct 14. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25312401
-
Enhancement of the production of Bacillus naganoensis pullulanase in recombinant Bacillus subtilis by integrative expression.Protein Expr Purif. 2019 Jul;159:42-48. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2019.03.006. Epub 2019 Mar 17. Protein Expr Purif. 2019. PMID: 30894325
-
Exploitation of the Escherichia coli lac operon promoter for controlled recombinant protein production.Biochem Soc Trans. 2019 Apr 30;47(2):755-763. doi: 10.1042/BST20190059. Epub 2019 Apr 10. Biochem Soc Trans. 2019. PMID: 30971435 Review.
-
Tunable recombinant protein expression in E. coli: promoter systems and genetic constraints.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017 Jan;101(2):501-512. doi: 10.1007/s00253-016-8045-z. Epub 2016 Dec 21. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 27999902 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Disorder prediction-based construct optimization improves activity and catalytic efficiency of Bacillus naganoensis pullulanase.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 19;6:24574. doi: 10.1038/srep24574. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27091115 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Restriction Protein, KlcAHS, Promotes Dissemination of Carbapenem Resistance.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 May 2;7:150. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00150. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28512626 Free PMC article.
-
Downsizing a pullulanase to a small molecule with improved soluble expression and secretion efficiency in Escherichia coli.Microb Cell Fact. 2016 Jan 14;15:9. doi: 10.1186/s12934-015-0403-5. Microb Cell Fact. 2016. PMID: 26762529 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary coupling saturation mutagenesis: Coevolution-guided identification of distant sites influencing Bacillus naganoensis pullulanase activity.FEBS Lett. 2020 Mar;594(5):799-812. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13652. Epub 2019 Nov 13. FEBS Lett. 2020. PMID: 31665817 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient extracellular expression of Bacillus deramificans pullulanase in Brevibacillus choshinensis.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016 Apr;43(4):495-504. doi: 10.1007/s10295-015-1719-1. Epub 2015 Dec 26. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26707948
References
-
- Singh RS, Saini GK, Kennedy JF (2010) Maltotriose syrup preparation from pullulan using pullulanase. Carbohydr Polym 80: 401-407. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.11.040. - DOI
-
- Hii SL, Ling TC, Mohamad R, Ariff AB (2009) Enhancement of extracellular pullulanase production by Raoultella planticola DSMZ 4617 using optimized medium based on sago starch. Open Biotechnol J 3: 1-8. doi:10.2174/1874070700903010001. - DOI
-
- Singh RS, Saini GK, Kennedy JF (2011) Continuous hydrolysis of pullulan using covalently immobilized pullulanase in a packed bed reactor. Carbohydr Polym 83: 672-675. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.08.037. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

