Friedreich's ataxia, frataxin, PIP5K1B: echo of a distant fracas
- PMID: 24194977
- PMCID: PMC3806116
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/725635
Friedreich's ataxia, frataxin, PIP5K1B: echo of a distant fracas
Abstract
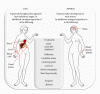
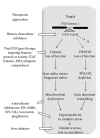
"Frataxin fracas" were the words used when referring to the frataxin-encoding gene (FXN) burst in as a motive to disqualify an alternative candidate gene, PIP5K1B, as an actor in Friedreich's ataxia (FRDA) (Campuzano et al., 1996; Cossee et al., 1997; Carvajal et al., 1996). The instrumental role in the disease of large triplet expansions in the first intron of FXN has been thereafter fully confirmed, and this no longer suffers any dispute (Koeppen, 2011). On the other hand, a recent study suggests that the consequences of these large expansions in FXN are wider than previously thought and that the expression of surrounding genes, including PIP5K1B, could be concurrently modulated by these large expansions (Bayot et al., 2013). This recent observation raises a number of important and yet unanswered questions for scientists and clinicians working on FRDA; these questions are the substratum of this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cis-silencing of PIP5K1B evidenced in Friedreich's ataxia patient cells results in cytoskeleton anomalies.Hum Mol Genet. 2013 Jul 15;22(14):2894-904. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt144. Epub 2013 Apr 2. Hum Mol Genet. 2013. PMID: 23552101
-
A GAA repeat expansion reporter model of Friedreich's ataxia recapitulates the genomic context and allows rapid screening of therapeutic compounds.Hum Mol Genet. 2013 Dec 20;22(25):5173-87. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt370. Epub 2013 Aug 13. Hum Mol Genet. 2013. PMID: 23943791 Free PMC article.
-
Friedreich's ataxia: new insights.Emerg Top Life Sci. 2023 Dec 14;7(3):313-323. doi: 10.1042/ETLS20230017. Emerg Top Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37698160 Review.
-
Mitochondrial damage and senescence phenotype of cells derived from a novel frataxin G127V point mutation mouse model of Friedreich's ataxia.Dis Model Mech. 2020 Jul 27;13(7):dmm045229. doi: 10.1242/dmm.045229. Dis Model Mech. 2020. PMID: 32586831 Free PMC article.
-
Friedreich ataxia: from GAA triplet-repeat expansion to frataxin deficiency.Am J Hum Genet. 2001 Jul;69(1):15-24. doi: 10.1086/321283. Epub 2001 Jun 4. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. PMID: 11391483 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Emerging antioxidant therapies in Friedreich's ataxia.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 6;15:1359618. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1359618. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38379897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative stress in inherited mitochondrial diseases.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Nov;88(Pt A):10-7. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.05.039. Epub 2015 Jun 12. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 26073122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expanded GAA repeats impede transcription elongation through the FXN gene and induce transcriptional silencing that is restricted to the FXN locus.Hum Mol Genet. 2015 Dec 15;24(24):6932-43. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddv397. Epub 2015 Sep 23. Hum Mol Genet. 2015. PMID: 26401053 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila melanogaster Models of Friedreich's Ataxia.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Apr 5;2018:5065190. doi: 10.1155/2018/5065190. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29850527 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Harding AE. Friedreich’s ataxia: a clinical and genetic study of 90 families with an analysis of early diagnostic criteria and intrafamilial clustering of clinical features. Brain. 1981;104(3):589–620. - PubMed
-
- Dürr A, Cossee M, Agid Y, et al. Clinical and genetic abnormalities in patients with Friedreich’s ataxia. The New England Journal of Medicine. 1996;335(16):1169–1175. - PubMed
-
- Bidichandani SI, Delatycki MB. Friedreich ataxia. In: Pagon RA, Adam MP, Bird TD, Dolan CR, Fong CT, Stephens K, editors. GeneReviews. 1993–2012. Seattle, Wash, USA: University of Washington; 1998. - PubMed
-
- de Castro M, García-Planells J, Monrós E, et al. Genotype and phenotype analysis of Friedreich’s ataxia compound heterozygous patients. Human Genetics. 2000;106(1):86–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

