Phytoestrogen α-Zearalanol attenuates homocysteine-induced apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- PMID: 24195080
- PMCID: PMC3806352
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/813450
Phytoestrogen α-Zearalanol attenuates homocysteine-induced apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells
Abstract
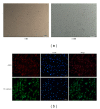
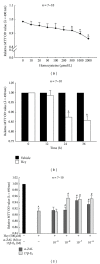
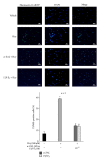
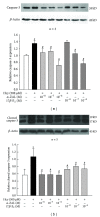
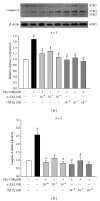
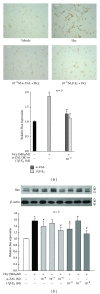
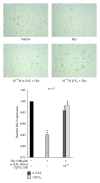
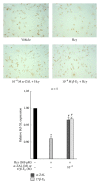
Hyperhomocysteinemia is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. The enhanced nitrative stress plays an important role in homocysteine-induced endothelial dysfunction. Previous studies have showed that phytoestrogen α -zearalanol alleviated endothelial injury in ovariectomized hyperhomocysteinemic rats; however, the underlying mechanism remains to be clarified. This study was to investigate the effects of α -zearalanol on homocysteine-induced endothelial apoptosis in vitro and explore the possible role of nitrative stress in these effects. Results showed that homocysteine (500 μ mol/L, 24 h) induced the apoptosis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) obviously, and this effect was significantly attenuated by pretreatment with α -zearalanol (10(-8)~10(-6) mol/L). Moreover, α -zearalanol downregulated proapoptotic protein Bax, upregulated antiapoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL, and decreased the expression and activity of caspase-9. These findings demonstrated that α -zearalanol could effectively alleviate homocysteine-induced endothelial apoptosis, and this antiapoptosis effect might be related to the inhibition of the intrinsic pathway. Western blot indicated an enhanced 3-nitrotyrosine expression in HUVECs when challenged with homocysteine, which was attenuated by pretreatment with α -zearalanol. This result implied that inhibition of nitrative stress might play a role in the protective effect of α -zearalanol on endothelial cells. Such discovery may shed a novel light on the antiatherogenic activities of α -zearalanol in hyperhomocysteinemia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alleviation of plasma homocysteine level by phytoestrogen α-zearalanol might be related to the reduction of cystathionine β-synthase nitration.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:143192. doi: 10.1155/2014/143192. Epub 2014 Mar 24. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24783194 Free PMC article.
-
Phytoestrogen alpha-zearalanol antagonizes homocysteine-induced imbalance of nitric oxide/endothelin-1 and apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2006;45(2):137-45. doi: 10.1385/CBB:45:2:137. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2006. PMID: 16757814
-
Phytoestrogen α-zearalanol improves vascular function in ovariectomized hyperhomocysteinemic rats.Atherosclerosis. 2011 Apr;215(2):309-15. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.12.029. Epub 2011 Jan 19. Atherosclerosis. 2011. PMID: 21292265
-
Upregulation of DAPK contributes to homocysteine-induced endothelial apoptosis via the modulation of Bcl2/Bax and activation of caspase 3.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Nov;14(5):4173-4179. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5733. Epub 2016 Sep 12. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27633052 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperhomocysteinemia as a Link of Chemotherapy-Related Endothelium Impairment.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2022 Oct;47(10):100932. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2021.100932. Epub 2021 Jul 24. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 34313228 Review.
Cited by
-
MiR-30b Is Involved in the Homocysteine-Induced Apoptosis in Human Coronary Artery Endothelial Cells by Regulating the Expression of Caspase 3.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Jul 31;16(8):17682-95. doi: 10.3390/ijms160817682. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26263983 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Zearalenone on Selected Hemostatic Parameters in Sexually Immature Gilts.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Sep 6;13(9):625. doi: 10.3390/toxins13090625. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34564628 Free PMC article.
-
Fundamental Mechanisms of the Cell Death Caused by Nitrosative Stress.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 20;9:742483. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.742483. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34616744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The preventive and therapeutic roles of phytoestrogen α-Zearalanol on osteoporetic rats due to ovariectomization.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2016 Nov;19(11):1216-1221. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27917278 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Atherosclerotic Effects of a Phytoestrogen-Rich Herbal Preparation in Postmenopausal Women.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Aug 11;17(8):1318. doi: 10.3390/ijms17081318. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27529226 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Antoniades C, Antonopoulos AS, Tousoulis D, Marinou K, Stefanadis C. Homocysteine and coronary atherosclerosis: from folate fortification to the recent clinical trials. European Heart Journal. 2009;30(1):6–15. - PubMed
-
- Kullo IJ, Ballantyne CM. Conditional risk factors for atherosclerosis. Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 2005;80(2):219–230. - PubMed
-
- Schulz E, Anter E, Keaney JF., Jr. Oxidative stress, antioxidants, and endothelial function. Current Medicinal Chemistry. 2004;11(9):1093–1104. - PubMed
-
- Suhara T, Fukuo K, Yasuda O, et al. Homocysteine enhances endothelial apoptosis via upregulation of Fas-mediated pathways. Hypertension. 2004;43(6):1208–1213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

