Safety and efficacy of long-term combination therapy with bezafibrate and ezetimibe in patients with dyslipidemia in the prospective, observational J-COMPATIBLE study
- PMID: 24195788
- PMCID: PMC4226247
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2840-12-163
Safety and efficacy of long-term combination therapy with bezafibrate and ezetimibe in patients with dyslipidemia in the prospective, observational J-COMPATIBLE study
Abstract
Background: There are numerous reports describing the efficacy of fenofibrate in combination with ezetimibe for treating dyslipidemia. In contrast, a study combining bezafibrate and ezetimibe has not yet been conducted. In this study, we examined the safety, including the risk of gallstone formation, and the efficacy of long-term combination therapy with bezafibrate and ezetimibe for treating dyslipidemia.
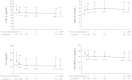
Methods: Dyslipidemic patients treated with 400 mg/day bezafibrate in combination with 10 mg/day ezetimibe for the first time were eligible. We selected 157 institutions in Japan and conducted a 12-month prospective observational study, with patients enrolled on the day they started combination therapy. Safety of the combination was examined in terms of the type, onset, and severity of adverse drug reactions (ADRs). Efficacy was evaluated in terms of the changes in low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C), triglyceride (TG), and non-HDL cholesterol (non-HDL-C) levels from the start of combination therapy (baseline) to the last observation carried forward (LOCF). Lipid levels were assessed at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months after starting combination therapy.
Results: We enrolled 665 patients in this observational study. Safety was evaluated in 659, and ADRs occurred in 42 patients (6.4%). The most frequent ADRs were blood creatine phosphokinase increase (1.5%) and myalgia (0.8%). Asymptomatic gallstones were observed in four patients (0.6%). Effectiveness was evaluated in 622 patients. LDL-C, HDL-C, TG, and non-HDL-C levels improved significantly from baseline to LOCF by -17.4%, 8.8%, -40.5%, and -21.6%, respectively (all, p < 0.001). Lipid levels also improved from baseline to each evaluation time-point.
Conclusions: Bezafibrate in combination with ezetimibe is safe and effective, and is potentially useful for comprehensive management of dyslipidemia.
Figures
References
-
- LaRosa JC, Grundy SM, Waters DD, Shear C, Barter P, Fruchart JC, Gotto AM, Greten H, Kastelein JJ, Shepherd J, Wenger NK. Treating to New Targets (TNT) Investigators. Intensive lipid lowering with atorvastatin in patients with stable coronary disease. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1425–1435. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa050461. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baigent C, Keech A, Kearney PM, Blackwell L, Buck G, Pollicino C, Kirby A, Sourjina T, Peto R, Collins R, Simes R. CholesterolTreatment Trialists’ (CTT) Collaborators. Efficacy and safety of cholesterol-lowering treatment: prospective meta-analysis of data from 90056 participants in 14 randomised trials of statins. Lancet. 2005;366:1267–1278. - PubMed
-
- Rubenfire M. Impact of Medical Subspecialty on Patient Compliance to Treatment Study Group. Safety and compliance with once-daily extended-release/lovastatin as initial therapy in the Impact of Medical Subspecialty on Patient Compliance to Treatment (IMPACT) study. Am J Cardiol. 2004;94:306–311. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2004.04.024. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ginsberg HN, Elam MB, Lovato LC, Crouse JR III, Leiter LA, Linz P, Friedewald WT, Buse JB, Gerstein HC, Probstfield J, Grimm RH, Ismail-Beigi F, Bigger JT, Goff DC Jr, Cushman WC, Simons-Morton DG, Byington RP. ACCORD Study Group. Effects of combination lipid therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1563–1574. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chapman MJ, Ginsberg HN, Amarenco P, Andreotti F, Borén J, Catapano AL, Descamps OS, Fisher E, Kovanen PT, Kuivenhoven JA, Lesnik P, Masana L, Nordestgaard BG, Ray KK, Reiner Z, Taskinen MR, Tokgözoglu L, Tybjærg-Hansen A, Watts GF. European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in patients at high risk of cardiovascular disease: evidence and guidance for management. Eur Heart J. 2011;32:1345–1361. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehr112. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

