In vivo evidence for cerebral bioenergetic abnormalities in schizophrenia measured using 31P magnetization transfer spectroscopy
- PMID: 24196348
- PMCID: PMC7461723
- DOI: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.2287
In vivo evidence for cerebral bioenergetic abnormalities in schizophrenia measured using 31P magnetization transfer spectroscopy
Abstract
Importance: Abnormalities in neural activity and cerebral bioenergetics have been observed in schizophrenia (SZ). Further defining energy metabolism anomalies would provide crucial information about molecular mechanisms underlying SZ and may be valuable for developing novel treatment strategies.
Objective: To investigate cerebral bioenergetics in SZ via measurement of creatine kinase activity using in vivo 31P magnetization transfer spectroscopy.
Design, setting, and participants: Cross-sectional case-control study in the setting of clinical services and a brain imaging center of an academic psychiatric hospital. Twenty-six participants with chronic SZ (including a subgroup diagnosed as having schizoaffective disorder) and 26 age-matched and sex-matched healthy control subjects (25 usable magnetic resonance spectroscopy data sets from the latter).
Intervention: 31P magnetization transfer spectroscopy.
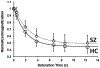
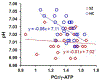
Main outcomes and measures: The primary outcome measure was the forward rate constant (k(f)) of the creatine kinase enzyme in the frontal lobe. We also collected independent measures of brain intracellular pH and steady-state metabolite ratios of high-energy phosphate-containing compounds (phosphocreatine and adenosine triphosphate [ATP]), inorganic phosphate, and the 2 membrane phospholipids phosphodiester and phosphomonoester.
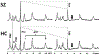
Results: A substantial (22%) and statistically significant (P = .003) reduction in creatine kinase kf was observed in SZ. In addition, intracellular pH was significantly reduced (7.00 in the SZ group vs 7.03 in the control group, P = .007) in this condition. The phosphocreatine to ATP ratio, inorganic phosphate to ATP ratio, and phosphomonoester to ATP ratio were not substantially altered in SZ, but a significant (P = .02) reduction was found in the phosphodiester to ATP ratio. The abnormalities were similar between SZ and schizoaffective disorder.
Conclusions and relevance: Using a novel 31P magnetization transfer magnetic resonance spectroscopy approach, we provide direct and compelling evidence for a specific bioenergetic abnormality in SZ. Reduced kf of the creatine kinase enzyme is consistent with an abnormality in storage and use of brain energy. The intracellular pH reduction suggests a relative increase in the contribution of glycolysis to ATP synthesis, providing convergent evidence for bioenergetic abnormalities in SZ. The similar phosphocreatine to ATP ratios in SZ and healthy controls suggest that the underlying bioenergetics abnormality is not associated with change in this metabolite ratio.
Figures
References
-
- Pettegrew JW, Minshew NJ. Molecular insights into schizophrenia. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1992;36:23–40. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Shachar D, Laifenfeld D. Mitochondria, synaptic plasticity, and schizophrenia. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2004;59:273–296. - PubMed
-
- Smesny S, Rosburg T, Nenadic I, et al. Metabolic mapping using 2D 31P-MR spectroscopy reveals frontal and thalamic metabolic abnormalities in schizophrenia. Neuroimage. April 1 2007;35(2):729–737. - PubMed
-
- Nenadic I, Langbein K, Weisbrod M, et al. 31P-MR spectroscopy in monozygotic twins discordant for schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Schizophr Res. Feb 2011;134(2-3):296–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

