Solid lipid nanoparticle-based calix[n]arenes and calix-resorcinarenes as building blocks: synthesis, formulation and characterization
- PMID: 24196356
- PMCID: PMC3856042
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms141121899
Solid lipid nanoparticle-based calix[n]arenes and calix-resorcinarenes as building blocks: synthesis, formulation and characterization
Abstract
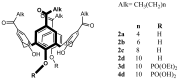
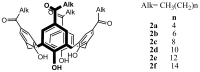
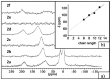
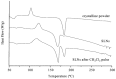
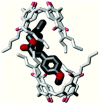
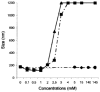
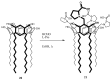
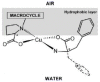
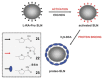
Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) have attracted increasing attention during recent years. This paper presents an overview about the use of calix[n]arenes and calix-resorcinarenes in the formulation of SLNs. Because of their specific inclusion capability both in the intraparticle spaces and in the host cavities as well as their capacity for functionalization, these colloidal nanostructures represent excellent tools for the encapsulation of different active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) in the area of drug targeting, cosmetic additives, contrast agents, etc. Various synthetic routes to the supramolecular structures will be given. These various routes lead to the formulation of the corresponding SLNs. Characterization, properties, toxicological considerations as well as numerous corresponding experimental studies and analytical methods will be also exposed and discussed.
Figures










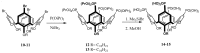






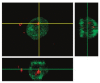

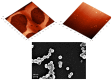
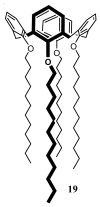


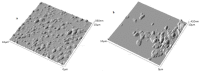





Similar articles
-
Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) derived from para-acyl-calix[9]-arene: preparation and stability.J Microencapsul. 2010;27(7):561-71. doi: 10.3109/02652048.2010.493620. J Microencapsul. 2010. PMID: 20923398
-
Calix[n]arenes as goldmines for the development of chemical entities of pharmaceutical interest.Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(36):6507-21. doi: 10.2174/13816128113199990406. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23656461 Review.
-
Characterization and stability of nanostructured lipid carriers as drug delivery system.Pak J Biol Sci. 2012 Feb 1;15(3):141-6. doi: 10.3923/pjbs.2012.141.146. Pak J Biol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22866544
-
Histological assessment of follicular delivery of flutamide by solid lipid nanoparticles: potential tool for the treatment of androgenic alopecia.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2016;42(6):846-53. doi: 10.3109/03639045.2015.1062896. Epub 2015 Jul 7. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2016. PMID: 26154267
-
Lipid nanocarriers: influence of lipids on product development and pharmacokinetics.Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 2011;28(4):357-93. doi: 10.1615/critrevtherdrugcarriersyst.v28.i4.20. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 2011. PMID: 21967401 Review.
Cited by
-
Positively Charged Nanostructured Lipid Carriers and Their Effect on the Dissolution of Poorly Soluble Drugs.Molecules. 2016 May 20;21(5):672. doi: 10.3390/molecules21050672. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27213324 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle drug delivery systems for synergistic delivery of tumor therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 16;14:1111991. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1111991. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36874010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid Nanoparticles for Ocular Gene Delivery.J Funct Biomater. 2015 Jun 8;6(2):379-94. doi: 10.3390/jfb6020379. J Funct Biomater. 2015. PMID: 26062170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Based on Monosubstituted Pillar[5]arenes: Chemoselective Synthesis of Macrocycles and Their Supramolecular Self-Assembly.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Nov 30;12(23):4266. doi: 10.3390/nano12234266. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36500889 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle-Based Contrast Agents for 129Xe HyperCEST NMR and MRI Applications.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2019 Nov 22;2019:9498173. doi: 10.1155/2019/9498173. eCollection 2019. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2019. PMID: 31819739 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wissing S.A., Kayser O., Muller R.H. Solid lipid nanoparticles for parenteral drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004;56:1257–1272. - PubMed
-
- Luks S., Muller R. EP0605497 A1. Medication vehicles made of solid lipid particles. 1992 Sep 16;
-
- Gasco M.R. U.S. Patent US5250236 A. Method for producing solid lipid microspheres having a narrow size distribution. 1993 Oct 5;
-
- Freitas C., Muller R.H. Effect of light and temperature on zeta potential and physical stability in solid lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 1998;168:221–229.
-
- Muller R.H., Mehnert W., Lucks J.S., Schwarz C., Zur Muhlen A., Meyhers H., Freitas C., Ruhl D. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN)-An alternative colloidal carrier system for controlled drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1995;41:62–65.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

