Safety and efficacy outcomes of first and second generation durable polymer drug eluting stents and biodegradable polymer biolimus eluting stents in clinical practice: comprehensive network meta-analysis
- PMID: 24196498
- PMCID: PMC3819044
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.f6530
Safety and efficacy outcomes of first and second generation durable polymer drug eluting stents and biodegradable polymer biolimus eluting stents in clinical practice: comprehensive network meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the safety and efficacy of durable polymer drug eluting stents (DES) and biodegradable polymer biolimus eluting stents (biolimus-ES).
Design: Network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.
Data sources and study selection: Medline, Google Scholar, Embase, and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) database search for randomised controlled trials comparing at least two of durable polymer sirolimus eluting stents (sirolimus-ES) and paclitaxel eluting stents (paclitaxel-ES), newer durable polymer everolimus eluting stents (everolimus-ES), Endeavor and Resolute zotarolimus eluting stents (zotarolimus-ES), and biodegradable polymer biolimus-ES.
Primary outcomes: Safety (death, myocardial infarction, definite or probable stent thrombosis) and efficacy (target lesion and target vessel revascularisation) assessed at up to one year and beyond.
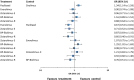
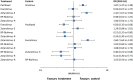
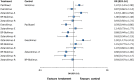
Results: 60 randomised controlled trials were compared involving 63,242 patients with stable coronary artery disease or acute coronary syndrome treated with a DES. At one year, there were no differences in mortality among devices. Resolute and Endeavor zotarolimus-ES, everolimus-ES, and sirolimus-ES, but not biodegradable polymer biolimus-ES, were associated with significantly reduced odds of myocardial infarction (by 29-34%) compared with paclitaxel-ES. Compared with everolimus-ES, biodegradable polymer biolimus-ES were associated with significantly increased odds of myocardial infarction (by 29%), while Endeavor zotarolimus-ES and paclitaxel-ES were associated with significantly increased odds of stent thrombosis. All investigated DES were similar with regards to efficacy endpoints, except for Endeavor zotarolimus-ES and paclitaxel-ES, which were associated with significantly increased the odds of target lesion and target vessel revascularisations compared with other devices. Direction of results beyond one year did not diverge from the findings for up to one year follow-up. Bayesian probability curves showed a gradient in the magnitude of effect, with everolimus-ES and Resolute zotarolimus-ES offering the highest safety profiles.
Conclusions: The newer durable polymer everolimus-ES and Resolute zotarolimus-ES and the biodegradable polymer biolimus-ES maintain the efficacy of sirolimus-ES; however, for safety endpoints, differences become apparent, with everolimus-ES and Resolute zotarolimus-ES emerging as the safest stents to date.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at
Figures




Comment in
-
Interventional cardiology: biodegradable-polymer DES versus second-generation durable-polymer DES.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2014 Jan;11(1):6. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2013.184. Epub 2013 Nov 26. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24275687 No abstract available.
References
-
- Camenzind E, Steg PG, Wijns W. Stent thrombosis late after implantation of first-generation drug-eluting stents: a cause for concern. Circulation 2007;115:1440-55. - PubMed
-
- Daemen J, Wenaweser P, Tsuchida K, Abrecht L, Vaina S, Morger C, et al. Early and late coronary stent thrombosis of sirolimus-eluting and paclitaxel-eluting stents in routine clinical practice: data from a large two-institutional cohort study. Lancet 2007;369:667-78. - PubMed
-
- Joner M, Finn AV, Farb A, Mont EK, Kolodgie FD, Ladich E, et al. Pathology of drug-eluting stents in humans: delayed healing and late thrombotic risk. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006;48:193-202. - PubMed
-
- Palmerini T, Biondi-Zoccai G, Della Riva D, Stettler C, Sangiorgi D, D’Ascenzo F, et al. Stent thrombosis with drug-eluting and bare-metal stents: evidence from a comprehensive network meta-analysis. Lancet 2012;379:1393-402. - PubMed
-
- Bangalore S, Kumar S, Fusaro M, Amoroso N, Attubato MJ, Feit F, et al. Short- and long-term outcomes with drug-eluting and bare-metal coronary stents: a mixed-treatment comparison analysis of 117 762 patient-years of follow-up from randomized trials. Circulation 2012;125:2873-91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
