Dedifferentiation of committed epithelial cells into stem cells in vivo
- PMID: 24196716
- PMCID: PMC4035230
- DOI: 10.1038/nature12777
Dedifferentiation of committed epithelial cells into stem cells in vivo
Abstract
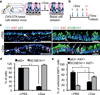
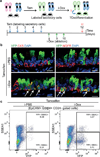
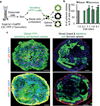
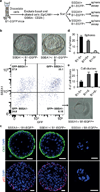
Cellular plasticity contributes to the regenerative capacity of plants, invertebrates, teleost fishes and amphibians. In vertebrates, differentiated cells are known to revert into replicating progenitors, but these cells do not persist as stable stem cells. Here we present evidence that differentiated airway epithelial cells can revert into stable and functional stem cells in vivo. After the ablation of airway stem cells, we observed a surprising increase in the proliferation of committed secretory cells. Subsequent lineage tracing demonstrated that the luminal secretory cells had dedifferentiated into basal stem cells. Dedifferentiated cells were morphologically indistinguishable from stem cells and they functioned as well as their endogenous counterparts in repairing epithelial injury. Single secretory cells clonally dedifferentiated into multipotent stem cells when they were cultured ex vivo without basal stem cells. By contrast, direct contact with a single basal stem cell was sufficient to prevent secretory cell dedifferentiation. In analogy to classical descriptions of amphibian nuclear reprogramming, the propensity of committed cells to dedifferentiate is inversely correlated to their state of maturity. This capacity of committed cells to dedifferentiate into stem cells may have a more general role in the regeneration of many tissues and in multiple disease states, notably cancer.
Figures
Comment in
-
Stem cells: Differentiated cells in a back-up role.Nature. 2013 Nov 14;503(7475):204-5. doi: 10.1038/nature12706. Epub 2013 Nov 6. Nature. 2013. PMID: 24196710 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wolff G. Entwicklungsphysiologische Studien. I. Die Regeneration der Urodelenlinse. Wilhelm Roux Arch. Entwickl. -Mech. Org. 1895;1:380–390.
-
- Brockes JP, Kumar A. Plasticity and reprogramming of differentiated cells in amphibian regeneration. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002;3:566–574. - PubMed
-
- Kai T, Spradling A. Differentiating germ cells can revert into functional stem cells in Drosophila melanogaster ovaries. Nature. 2004;428:564–569. - PubMed
-
- Slack JMW. Metaplasia and transdifferentiation: from pure biology to the clinic. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007;8:369–378. - PubMed
-
- Kragl M, et al. Cells keep a memory of their tissue origin during axolotl limb regeneration. Nature. 2009;460:60–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

