Wild-type and innate immune-deficient mice are not susceptible to the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus
- PMID: 24197535
- PMCID: PMC3917065
- DOI: 10.1099/vir.0.060640-0
Wild-type and innate immune-deficient mice are not susceptible to the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus
Abstract
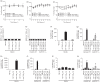
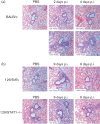
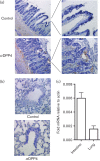
The Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) is a newly emerging highly pathogenic virus causing almost 50 % lethality in infected individuals. The development of a small-animal model is critical for the understanding of this virus and to aid in development of countermeasures against MERS-CoV. We found that BALB/c, 129/SvEv and 129/SvEv STAT1 knockout mice are not permissive to MERS-CoV infection. The lack of infection may be due to the low level of mRNA and protein for the MERS-CoV receptor, dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4), in the lungs of mice. The low level of DPP4 in the lungs likely contributes to the lack of viral replication in these mouse models and suggests that a transgenic mouse model expressing DPP4 to higher levels is necessary to create a mouse model for MERS-CoV.
Figures
References
-
- Chan J. F., Chan K. H., Choi G. K., To K. K., Tse H., Cai J. P., Yeung M. L., Cheng V. C., Chen H. & other authors (2013). Differential cell line susceptibility to the emerging novel human betacoronavirus 2c EMC/2012: implications for disease pathogenesis and clinical manifestation. J Infect Dis 207, 1743–1752 10.1093/infdis/jit123 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Corman V. M., Eckerle I., Bleicker T., Zaki A., Landt O., Eschbach-Bludau M., van Boheemen S., Gopal R., Ballhause M. & other authors (2012a). Detection of a novel human coronavirus by real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction. Eurosurveillance 17, 39. - PubMed
-
- Corman V. M., Muller M. A., Costabel U., Timm J., Binger T., Meyer B., Kreher P., Lattwein E., Eschbach-Bludau M. & other authors (2012b). Assays for laboratory confirmation of novel human coronavirus (hCoV-EMC) infections. Eurosurveillance 17, 49 - PubMed
-
- de Wit E., Prescott J., Baseler L., Bushmaker T., Thomas T., Lackemeyer M. G., Martellaro C., Milne-Price S., Haddock E. & other authors (2013). The Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) does not replicate in Syrian hamsters. PLoS ONE 8, e69127 10.1371/journal.pone.0069127 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Drosten C., Seilmaier M., Corman V. M., Hartmann W., Scheible G., Sack S., Guggemos W., Kallies R., Muth D. & other authors (2013). Clinical features and virological analysis of a case of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection. Lancet Infect Dis 13, 745–751 10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70154-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

