GTP-binding proteins mediate transmitter inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium channels
- PMID: 2419757
- PMCID: PMC2926796
- DOI: 10.1038/319670a0
GTP-binding proteins mediate transmitter inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium channels
Abstract
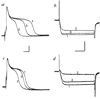
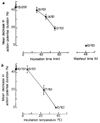
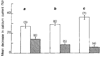
The modulation of voltage-dependent calcium channels by hormones and neurotransmitters has important implications for the control of many Ca2+-dependent cellular functions including exocytosis and contractility. We made use of electrophysiological techniques, including whole-cell patch-clamp recordings from dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurones, to demonstrate a role for GTP-binding proteins (G-proteins) as signal transducers in the noradrenaline- and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-induced inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium channels. This action of the transmitters was blocked by: (1) preincubation of the cells with pertussis toxin (a bacterial exotoxin catalysing ADP-ribosylation of G-proteins); or (2) intracellular administration of guanosine 5'-O-(2-thiodiphosphate) (GDP-beta-S), a non-hydrolysable analogue of GDP that competitively inhibits the binding of GTP to G-proteins. Our findings provide the first direct demonstration of the G-protein-mediated inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium channels by neurotransmitters. This mode of transmitter action may explain the ability of noradrenaline and GABA to presynaptically inhibit Ca2+-dependent neurosecretion from DRG sensory neurones.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Calcium channel currents and their inhibition by (-)-baclofen in rat sensory neurones: modulation by guanine nucleotides.J Physiol. 1987 May;386:1-17. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016518. J Physiol. 1987. PMID: 2445960 Free PMC article.
-
On the role of endogenous G-protein beta gamma subunits in N-type Ca2+ current inhibition by neurotransmitters in rat sympathetic neurones.J Physiol. 1998 Jan 15;506 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):319-29. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.319bw.x. J Physiol. 1998. PMID: 9490860 Free PMC article.
-
A guanine nucleotide-binding protein mediates the inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium current by somatostatin in a pituitary cell line.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9035-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9035. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986. PMID: 2431411 Free PMC article.
-
G proteins couple alpha-adrenergic and GABAb receptors to inhibition of peptide secretion from peripheral sensory neurons.J Neurosci. 1989 Feb;9(2):657-66. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-02-00657.1989. J Neurosci. 1989. PMID: 2465394 Free PMC article.
-
Pertussis toxin-sensitive G-proteins: participation in the modulation of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels by hormones and neurotransmitters.Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1990;24:89-94. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1990. PMID: 1976337 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 6 signaling enhances TRPM1 calcium channel function and increases melanin content in human melanocytes.Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2013 May;26(3):348-56. doi: 10.1111/pcmr.12083. Epub 2013 Mar 27. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2013. PMID: 23452348 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Ca-channel current by an adenosine analog mediated by a GTP-binding protein in chick sensory neurons.Pflugers Arch. 1989 Jun;414(2):145-9. doi: 10.1007/BF00580956. Pflugers Arch. 1989. PMID: 2547194
-
Frequency-dependent depression of inhibition in guinea-pig neocortex in vitro by GABAB receptor feed-back on GABA release.J Physiol. 1989 May;412:513-41. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017629. J Physiol. 1989. PMID: 2557431 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory and stimulatory G proteins of adenylate cyclase: cDNA and amino acid sequences of the alpha chains.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6687-91. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6687. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986. PMID: 3092218 Free PMC article.
-
ATP regulates muscarine-sensitive potassium current in dissociated bull-frog primary afferent neurones.J Physiol. 1990 Jul;426:241-64. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018136. J Physiol. 1990. PMID: 2121960 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kupferman I. A. Rev. Neurosci. 1979;2:447–465. - PubMed
-
- Shain W, Carpenter DO. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 1981;22:205–250. - PubMed
-
- Dunlap K. In: The Mechanism of Gated Calcium Transport across Biological Membranes. Ohnishi ST, Endo M, editors. New York: Academic; 1981. pp. 87–97.
-
- Fischbach GD, Dunlap K, Mudge AW, Leeman S. In: Neurosecretion and Brain Peptides. Martin JB, Reichlin S, Bick KL, editors. New York: Raven; 1981. pp. 175–188.
-
- Holz GG, Kream RM, Dunlap K. Soc. Neurosci Abstr. 1985;11:126.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

