Practice variability in brain death determination: a call to action
- PMID: 24198290
- PMCID: PMC3854834
- DOI: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000436938.70528.4a
Practice variability in brain death determination: a call to action
Abstract
Objective: To characterize the present state of brain death (BD) determination in actual practice relative to contemporary American Academy of Neurology (AAN) guidelines.
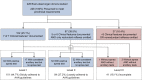
Methods: We reviewed the charts of all adult (16 years and older) BD organ donors during 2011 from 68 heterogeneous hospitals in the Midwest United States. Data were collected across 5 categories: guideline performance, preclinical testing, clinical examination, apnea testing, and use of ancillary tests. Practice within categories and overall adherence to AAN guidelines were assessed.
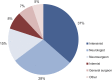
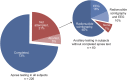
Results: Two hundred twenty-six BD organ donors were included. Practice exceeded recommendations in guideline performance but varied widely and deviated from AAN guidelines in all other categories. One hundred two (45.1%) had complete documentation of brainstem areflexia and absent motor response. One hundred sixty-six (73.5%) had completed apnea testing. Of the 60 without completed apnea testing, 56 (93.3%) had ancillary tests consistent with BD. Overall, 101 (44.7%) strictly and 84 (37.2%) loosely adhered to contemporary AAN guidelines.
Conclusions: There is wide variability in the documentation of BD determination, likely reflecting similar variability in practice. This is a call for improved documentation, better uniformity of policies, and comprehensive and strategically targeted educational initiatives to ensure consistently contemporary approaches to BD determination in every patient.
Figures
Comment in
-
Practice variability in brain death determination: a call to action.Neurology. 2014 May 27;82(21):1936-7. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000450702.68005.e9. Neurology. 2014. PMID: 24862897 No abstract available.
-
Practice variability in brain death determination: a call to action.Neurology. 2014 Jun 3;82(22):2040. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000401. Neurology. 2014. PMID: 24891543 No abstract available.
-
Author response.Neurology. 2014 May 27;82(21):1937. Neurology. 2014. PMID: 24991658 No abstract available.
-
Author response.Neurology. 2014 Jun 3;82(22):2040-1. Neurology. 2014. PMID: 25013885 No abstract available.
References
-
- Guidelines for the determination of death: report of the medical consultants on the diagnosis of death to the President's Commission for the Study of Ethical Problems in Medicine and Biomedical and Behavioral Research. JAMA 1981;246:2184–2186 - PubMed
-
- Wijdicks EF. Brain death worldwide: accepted fact but no global consensus in diagnostic criteria. Neurology 2002;58:20–25 - PubMed
-
- Practice parameters for determining brain death in adults (summary statement). The Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 1995;45:1012–1014 - PubMed
-
- Wijdicks EF, Varelas PN, Gronseth GS, et al. ; American Academy of Neurology Evidence-based guideline update: determining brain death in adults—report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2010;74:1911–1918 - PubMed
-
- Greer DM, Varelas PN, Haque S, et al. Variability of brain death determination guidelines in leading US neurologic institutions. Neurology 2008;70:284–289 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
