Inhibition of arenavirus by A3, a pyrimidine biosynthesis inhibitor
- PMID: 24198417
- PMCID: PMC3911634
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02275-13
Inhibition of arenavirus by A3, a pyrimidine biosynthesis inhibitor
Abstract
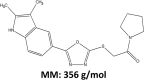
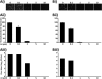
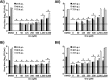
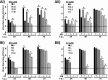
Arenaviruses merit significant interest as important human pathogens, since several of them cause severe hemorrhagic fever disease that is associated with high morbidity and significant mortality. Currently, there are no FDA-licensed arenavirus vaccines available, and current antiarenaviral therapy is limited to an off-labeled use of the nucleoside analog ribavirin, which has limited prophylactic efficacy. The pyrimidine biosynthesis inhibitor A3, which was identified in a high-throughput screen for compounds that blocked influenza virus replication, exhibits a broad-spectrum antiviral activity against negative- and positive-sense RNA viruses, retroviruses, and DNA viruses. In this study, we evaluated the antiviral activity of A3 against representative Old World (lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus) and New World (Junin virus) arenaviruses in rodent, monkey, and human cell lines. We show that A3 is significantly more efficient than ribavirin in controlling arenavirus multiplication and that the A3 inhibitory effect is in part due to its ability to interfere with viral RNA replication and transcription. We document an additive antiarenavirus effect of A3 and ribavirin, supporting the potential combination therapy of ribavirin and pyrimidine biosynthesis inhibitors for the treatment of arenavirus infections.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Recombinant Pichinde reporter virus as a safe and suitable surrogate for high-throughput antiviral screening against highly pathogenic arenaviruses.Antiviral Res. 2025 Apr;236:106117. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2025.106117. Epub 2025 Feb 17. Antiviral Res. 2025. PMID: 39970958
-
Mining a Kröhnke Pyridine Library for Anti-Arenavirus Activity.ACS Infect Dis. 2018 May 11;4(5):815-824. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.7b00236. Epub 2018 Mar 1. ACS Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29405696
-
Arenavirus Quasispecies and Their Biological Implications.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2016;392:231-76. doi: 10.1007/82_2015_468. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26472215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Clotrimazole Derivatives as Specific Inhibitors of Arenavirus Fusion.J Virol. 2019 Mar 5;93(6):e01744-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01744-18. Print 2019 Mar 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30626681 Free PMC article.
-
Reverse genetics approaches to combat pathogenic arenaviruses.Antiviral Res. 2008 Dec;80(3):239-50. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2008.08.002. Epub 2008 Sep 7. Antiviral Res. 2008. PMID: 18782590 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Broad Antiviral Strategy: Inhibitors of Human DHODH Pave the Way for Host-Targeting Antivirals against Emerging and Re-Emerging Viruses.Viruses. 2022 Apr 28;14(5):928. doi: 10.3390/v14050928. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35632670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Broad-spectrum agents for flaviviral infections: dengue, Zika and beyond.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017 Aug;16(8):565-586. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2017.33. Epub 2017 May 5. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017. PMID: 28473729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Original Chemical Series of Pyrimidine Biosynthesis Inhibitors That Boost the Antiviral Interferon Response.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Sep 22;61(10):e00383-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00383-17. Print 2017 Oct. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28807907 Free PMC article.
-
Reporter-Expressing, Replicating-Competent Recombinant Arenaviruses.Viruses. 2016 Jul 20;8(7):197. doi: 10.3390/v8070197. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27447662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hemorrhagic Fever-Causing Arenaviruses: Lethal Pathogens and Potent Immune Suppressors.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 13;10:372. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00372. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30918506 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Buchmeier MJ, Peters CJ, de la Torre JC. 2007. Arenaviridae: the viruses and their replication, p 1792–1827 In Fields BN, Knipe DM, Howley PM. (ed), Fields virology, 5th ed, vol 2 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32-GM-68411-8/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21NS075611-01/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI081773/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI049815/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI081773/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32-AI-049815/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS075611/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN266200700008C/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AI099681/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI079665/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN272201000055C/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI077719/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R03AI099681-01A1/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI081773/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM068411/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI047140/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

