Pazopanib and anti-VEGF therapy
- PMID: 24198612
- PMCID: PMC3818876
Pazopanib and anti-VEGF therapy
Abstract
Pazopanib (Votrient™, GlaxoSmithKline), a multi-kinase inhibitor with activity against VEGFR and other receptors, was recently approved by the FDA for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Here, we review the history of its development, together with an overview of VEGF and its receptors and co-receptors. Results from selected clinical trial data in RCC and other malignant diseases are presented. Based on available evidence, pazopanib is an effective VEGFR inhibitor with demonstrable clinical activity in metastatic RCC and promising activity in other diseases. Like most kinase inhibitors, its activity is not restricted to VEGF receptors, which is reflected in its side-effect profile.
Keywords: VEGFR; pazopanib; renal cell carcinoma.
Figures
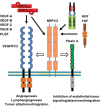
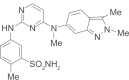
References
-
- Yang JC. Bevacizumab for patients with metastatic renal cancer: an update. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(18 Pt 2):6367S–70S. - PubMed
-
- Woolard J, Wang WY, Bevan HS, et al. VEGF165b, an inhibitory vascular endothelial growth factor splice variant: mechanism of action, in vivo effect on angiogenesis and endogenous protein expression. Cancer Res. 2004;64(21):7822–7835. - PubMed
-
- Shibuya M, Claesson-Welsh L. Signal transduction by VEGF receptors in regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Exp Cell Res. 2006;312(5):549–560. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
