Obstructive renal injury: from fluid mechanics to molecular cell biology
- PMID: 24198613
- PMCID: PMC3818880
- DOI: 10.2147/rru.s6597
Obstructive renal injury: from fluid mechanics to molecular cell biology
Abstract
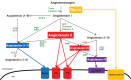
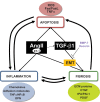
Urinary tract obstruction is a frequent cause of renal impairment. The physiopathology of obstructive nephropathy has long been viewed as a mere mechanical problem. However, recent advances in cell and systems biology have disclosed a complex physiopathology involving a high number of molecular mediators of injury that lead to cellular processes of apoptotic cell death, cell injury leading to inflammation and resultant fibrosis. Functional studies in animal models of ureteral obstruction using a variety of techniques that include genetically modified animals have disclosed an important role for the renin-angiotensin system, transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) and other mediators of inflammation in this process. In addition, high throughput techniques such as proteomics and transcriptomics have identified potential biomarkers that may guide clinical decision-making.
Keywords: fluid mechanics; molecular cell biology; renal injury; urinary tract obstruction.
Figures
References
-
- Thomas D. Fetal uropathy. Br J Urol. 1990;66(3):225–231. - PubMed
-
- NAPRTCS . North American Pediatric Renal Trials and Collaborative Studies, 2008 Annual Report. Rockville, MD: EMMES; 2008.
-
- Lewis M, Shaw J, Reid C, Evans J, Webb N, Verrier-Jones K. Demography and management of childhood established renal failure in the UK (chapter 13) Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007;22(Suppl 7):vii165–vii175. - PubMed
-
- Kaufman J, Dhakal M, Patel B, Hamburger R. Community-acquired acute renal failure. Am J Kidney Dis. 1991;17(2):191–198. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

