Four-year follow-up of endoscopic gastroplication for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease
- PMID: 24199028
- PMCID: PMC3817287
- DOI: 10.4292/wjgpt.v4.i4.120
Four-year follow-up of endoscopic gastroplication for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the long-term effect of Endocinch treatment for gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Methods: After unblinding and crossover, 50 patients (32 males, 18 females; mean age 46 years) with pH-proven chronic GERD were recruited from an initial randomized, placebo-controlled, single-center study, and included in the present prospective open-label follow-up study. Initially, three gastroplications using the Endocinch device were placed under deep sedation in a standardized manner. Optional retreatment was offered in the first year with 1 or 2 extra gastroplications. At baseline, 3 mo after (re) treatment and yearly proton pump inhibitor (PPI) use, GERD symptoms, quality of life (QoL) scores, adverse events and treatment failures (defined as: patients using > 50% of their baseline PPI dose or receiving alternative antireflux therapy) were assessed. Intention-to-treat analysis was performed.
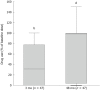
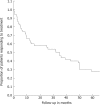
Results: Median follow-up was 48 mo [interquartile range (IQR): 38-52]. Three patients were lost to follow-up. In 44% of patients retreatment was done after a median of 4 mo (IQR: 3-8). No serious adverse events occurred. At the end of follow-up, symptom scores and 4 out of 6 QoL subscales were improved (all P < 0.01 compared to baseline). However, 80% of patients required PPIs for their GERD symptoms. Ultimately, 64% of patients were classified as treatment failures. In 60% a post-procedural endoscopy was carried out, of which in 16% reflux esophagitis was diagnosed.
Conclusion: In the 4-year follow-up period, the subset of GERD patients that benefit from endoscopic gastroplication kept declining gradually, nearly half opted for retreatment and 80% required PPIs eventually.
Keywords: Endocinch; Endoscopic therapy; Follow-up studies; Gastroesophageal Reflux; Gastroplication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Use of an endoscopic suturing device (the "ESD") to treat patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease, after unsuccessful EndoCinch endoluminal gastroplication: another failure.Endoscopy. 2005 Aug;37(8):700-5. doi: 10.1055/s-2005-870128. Endoscopy. 2005. PMID: 16032486
-
A one-year follow-up study of endoluminal gastroplication (Endocinch) in GERD patients refractory to proton pump inhibitor therapy.Dig Dis Sci. 2005 Feb;50(2):351-6. doi: 10.1007/s10620-005-1610-4. Dig Dis Sci. 2005. PMID: 15745100
-
Long-term benefit of transoral incisionless fundoplication using the esophyx device for the management of gastroesophageal reflux disease responsive to medical therapy.Dis Esophagus. 2017 Feb 1;30(3):1-8. doi: 10.1111/dote.12525. Dis Esophagus. 2017. PMID: 27868281
-
Lower esophageal sphincter injections for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease.Thorac Surg Clin. 2005 Aug;15(3):405-15. doi: 10.1016/j.thorsurg.2005.04.001. Thorac Surg Clin. 2005. PMID: 16104131 Review.
-
Management of gastroesophageal reflux disease: medications, surgery, or endoscopic therapy? (Current status and trends).J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2005;15(4):375-88. doi: 10.1615/jlongtermeffmedimplants.v15.i4.50. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2005. PMID: 16022648 Review.
Cited by
-
Advanced Endoscopic Imaging and Interventions in GERD: An Update and Future Directions.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Nov 29;8:728696. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.728696. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34912815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in the evaluation and management of esophageal disease of systemic sclerosis.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2015 Jan;17(1):475. doi: 10.1007/s11926-014-0475-y. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25475597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developments in flexible endoscopic surgery: a review.Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2014 Dec 18;8:31-42. doi: 10.2147/CEG.S46584. eCollection 2015. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25565878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy in Pediatric Gastroenterology.Front Pediatr. 2022 Feb 25;9:715912. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.715912. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35280448 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Herwaarden MA, Samsom M, Smout AJ. The role of hiatus hernia in gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004;16:831–835. - PubMed
-
- Chen YK, Raijman I, Ben-Menachem T, Starpoli AA, Liu J, Pazwash H, Weiland S, Shahrier M, Fortajada E, Saltzman JR, et al. Long-term outcomes of endoluminal gastroplication: a U.S. multicenter trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;61:659–667. - PubMed
-
- Ozawa S, Kumai K, Higuchi K, Arakawa T, Kato M, Asaka M, Katada N, Kuwano H, Kitajima M. Short-term and long-term outcome of endoluminal gastroplication for the treatment of GERD: the first multicenter trial in Japan. J Gastroenterol. 2009;44:675–684. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

