The microbiology of olive mill wastes
- PMID: 24199199
- PMCID: PMC3809369
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/784591
The microbiology of olive mill wastes
Abstract
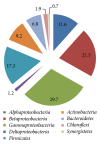
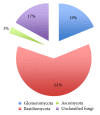
Olive mill wastes (OMWs) are high-strength organic effluents, which upon disposal can degrade soil and water quality, negatively affecting aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. The main purpose of this review paper is to provide an up-to-date knowledge concerning the microbial communities identified over the past 20 years in olive mill wastes using both culture-dependent and independent approaches. A database survey of 16S rRNA gene sequences (585 records in total) obtained from olive mill waste environments revealed the dominance of members of Alphaproteobacteria, Betaproteobacteria, Gammaproteobacteria, Firmicutes, and Actinobacteria. Independent studies confirmed that OMW microbial communities' structure is cultivar dependent. On the other hand, the detection of fecal bacteria and other potential human pathogens in OMWs is of major concern and deserves further examination. Despite the fact that the degradation and detoxification of the olive mill wastes have been mostly investigated through the application of known bacterial and fungal species originated from other environmental sources, the biotechnological potential of indigenous microbiota should be further exploited in respect to olive mill waste bioremediation and inactivation of plant and human pathogens. The implementation of omic and metagenomic approaches will further elucidate disposal issues of olive mill wastes.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Olive mill waste sludge: From permanent pollution to a highly beneficial organic biofertilizer: A critical review and future perspectives.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023 Jul 1;259:114997. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.114997. Epub 2023 May 19. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023. PMID: 37210993 Review.
-
Olive mill wastes: from wastes to resources.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Mar;31(14):20853-20880. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-32468-x. Epub 2024 Feb 26. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38407704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Raw and Bioaugmented Olive-Mill Wastewater and Olive-Mill Solid Waste on the Content of Photosynthetic Molecules in Tobacco Plants.J Agric Food Chem. 2016 Aug 3;64(30):5971-84. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b00725. Epub 2016 Jul 20. J Agric Food Chem. 2016. PMID: 27399282
-
Microbial Community Succession and Organic Pollutants Removal During Olive Mill Waste Sludge and Green Waste Co-composting.Front Microbiol. 2022 Feb 21;12:814553. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.814553. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35265049 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial intervention improves pollutant removal and semi-liquid organo-mineral fertilizer production from olive mill wastewater sludge and rock phosphate.J Environ Manage. 2024 Mar;354:120317. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.120317. Epub 2024 Feb 22. J Environ Manage. 2024. PMID: 38387346
Cited by
-
Valorization of Olive Mill Wastewater by Selective Sequential Fermentation.Foods. 2025 Jun 21;14(13):2170. doi: 10.3390/foods14132170. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40646922 Free PMC article.
-
Effective Detoxification of Olive Mill Wastewater Using Multi-Step Surfactant-Based Treatment: Assessment of Environmental and Health Impact.Molecules. 2024 Sep 10;29(18):4284. doi: 10.3390/molecules29184284. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39339279 Free PMC article.
-
Quality Assessment of Waste from Olive Oil Production and Design of Biodegradable Packaging.Foods. 2022 Nov 23;11(23):3776. doi: 10.3390/foods11233776. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36496585 Free PMC article.
-
Olive Pomace Extract Acts as a New Potent Ferroptosis Inhibitor in Human Cells.Molecules. 2025 Jul 24;30(15):3095. doi: 10.3390/molecules30153095. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40807270 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Pomace Matrix and Cyclodextrin Encapsulation on Olive Pomace Polyphenols' Bioaccessibility and Intestinal Permeability.Nutrients. 2020 Feb 29;12(3):669. doi: 10.3390/nu12030669. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32121413 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Morillo JA, Aguilera M, Antízar-Ladislao B, et al. Molecular microbial and chemical investigation of the bioremediation of two-phase olive mill waste using laboratory-scale bioreactors. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 2008;79(2):309–317. - PubMed
-
- International Olive Oil Council. 2008, http://www.internationaloliveoil.org/
-
- Uceda M, Jiménez A, Beltrán G. Olive oil extraction and quality. Grasas y Aceites. 2006;57(1):25–31.
-
- Ntougias S, Zervakis GI, Ehaliotis C, Kavroulakis N, Papadopoulou KK. Ecophysiology and molecular phylogeny of bacteria isolated from alkaline two-phase olive mill wastes. Research in Microbiology. 2006;157(4):376–385. - PubMed
-
- Hafidi M, Amir S, Revel J-C. Structural characterization of olive mill waster-water after aerobic digestion using elemental analysis, FTIR and 13C NMR. Process Biochemistry. 2005;40(8):2615–2622.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

