Dual ALK and EGFR inhibition targets a mechanism of acquired resistance to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor crizotinib in ALK rearranged lung cancer
- PMID: 24199682
- PMCID: PMC3947244
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2013.09.019
Dual ALK and EGFR inhibition targets a mechanism of acquired resistance to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor crizotinib in ALK rearranged lung cancer
Abstract
Introduction: The multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) crizotinib is active against ALK translocated non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC); however acquired resistance invariably develops over time. ALK mutations have previously been implicated in only a third of resistant tumors. We sought to evaluate alternative mechanisms of resistance and preclinical strategies to overcome these in a cell line driven by EML4-ALK.
Methods: We selected the NSCLC cell line NCI-H3122 (H3122: EML4-ALK E13;A20) and derived resistant variants that were able to grow in the presence of 1 μM crizotinib. These were analyzed for ALK mutations, sensitivity to crizotinib in combination with other TKIs, and for activation of alternative tyrosine kinases.
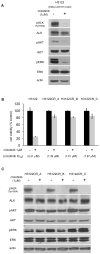
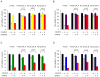
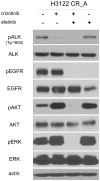
Results: All H3122 crizotinib resistant (CR) clones lacked amplification or mutations in the kinase domain of ALK. To evaluate if possible alternative kinases functioned as "bypass" tracks for downstream signaling activation in these resistance cells, we performed of phosho-receptor tyrosine kinase array that demonstrated that CR clones had higher phospho-EGFR signals than H3122 cells before and after exposure to crizotinib. A functional approach of dual ALK TKI (with crizotinib) with combinatory TKI inhibition was used as a secondary screen for possible targets. Crizotinib+erlotinib (reversible EGFR TKI) and crizotinib+afatinib (irreversible EGFR/ERBB2 TKI) were able to inhibit the growth of H3122 CR clones, confirming EGFR activation as a mechanism of resistance. The removal of crizotinib from the culture media re-sensitized CR cells to crizotinib.
Conclusions: We identified activation of EGFR as a mechanism of resistance to crizotinib in preclinical models of ALK translocated NSCLC. If EGFR activation is confirmed as a predominant mechanism of ALK TKI-induced resistance in patient-derived tumors, the use of ALK plus EGFR TKIs could be explored for this important cohort of NSCLCs.
Keywords: Anaplastic lymphoma kinase; Crizotinib; Epidermal growth factor receptor; Kinase inhibitor; Non-small-cell lung cancer; Tyrosine kinase.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Daniel B. Costa has received consulting fees from Pfizer, Roche and AstraZeneca. Norihiro Yamaguchi, Antonio R. Lucena-Araujo, Sohei Nakayama, Lorena L. de Figueiredo-Pontes, David A. Gonzalez, Hiroyuki Yasuda and Susumu Kobayashi have no conflicts to disclose. No other conflict of interest is stated.
Figures

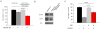
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63(1):11–30. - PubMed
-
- Pao W, Girard N. New driver mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12(2):175–180. - PubMed
-
- Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S, Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S, et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 2007;448(7153):561–566. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

