Improving low-dose blood-brain barrier permeability quantification using sparse high-dose induced prior for Patlak model
- PMID: 24200529
- PMCID: PMC4188431
- DOI: 10.1016/j.media.2013.09.008
Improving low-dose blood-brain barrier permeability quantification using sparse high-dose induced prior for Patlak model
Abstract
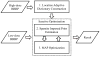
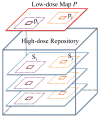
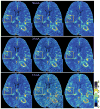
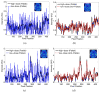
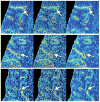
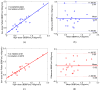
Blood-brain barrier permeability (BBBP) measurements extracted from the perfusion computed tomography (PCT) using the Patlak model can be a valuable indicator to predict hemorrhagic transformation in patients with acute stroke. Unfortunately, the standard Patlak model based PCT requires excessive radiation exposure, which raised attention on radiation safety. Minimizing radiation dose is of high value in clinical practice but can degrade the image quality due to the introduced severe noise. The purpose of this work is to construct high quality BBBP maps from low-dose PCT data by using the brain structural similarity between different individuals and the relations between the high- and low-dose maps. The proposed sparse high-dose induced (shd-Patlak) model performs by building a high-dose induced prior for the Patlak model with a set of location adaptive dictionaries, followed by an optimized estimation of BBBP map with the prior regularized Patlak model. Evaluation with the simulated low-dose clinical brain PCT datasets clearly demonstrate that the shd-Patlak model can achieve more significant gains than the standard Patlak model with improved visual quality, higher fidelity to the gold standard and more accurate details for clinical analysis.
Keywords: Blood–brain barrier permeability; Patlak model; Radiation dose reduction; Sparse high-dose induced prior.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Andersen I, Szymkowiak A, Rasmussen C, Hanson L, Marstrand J, Larsson H, Hansen L. Perfusion quantification using Gaussian process deconvolution. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2002;48:351–361. - PubMed
-
- Bisdas S, Hartel M, Cheong L, Koh T, Vogl T. Prediction of subsequent hemorrhage in acute ischemic stroke using permeability CT imaging and a distributed parameter tracer kinetic model. Journal of neuroradiology. 2007;34:101–108. - PubMed
-
- Britten A, Crotty M, Kiremidjian H, Grundy A, Adam E. The addition of computer simulated noise to investigate radiation dose and image quality in images with spatial correlation of statistical noise: an example application to X-ray CT of the brain. British journal of radiology. 2004;77:323–328. - PubMed
-
- Calamante F, Gadian D, Connelly A. Quantification of bolus-tracking MRI: Improved characterization of the tissue residue function using Tikhonov regularization. Magnetic resonance in medicine. 2003;50:1237–1247. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

