Validation of C-reactive protein levels as a prognostic indicator for survival in a large cohort of pancreatic cancer patients
- PMID: 24201751
- PMCID: PMC3887299
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2013.701
Validation of C-reactive protein levels as a prognostic indicator for survival in a large cohort of pancreatic cancer patients
Abstract
Background: Recent evidence indicates that the host inflammatory response has an important role in the tumour progression. Elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) levels have been previously associated with poor prognosis in several cancer types including small-scale studies in pancreatic cancer (PC) patients. The purpose of the present study was to validate the prognostic impact of plasma CRP levels at date of diagnosis on cancer-specific survival (CSS) in a large cohort of PC patients.
Methods: Data from 474 consecutive patients with adenocarcinoma of the pancreas, treated between 2004 and 2012 at a single centre, were evaluated retrospectively. CSS was analysed using the Kaplan-Meier method. To evaluate the prognostic significance of plasma CRP levels, univariate and multivariate Cox analyses were applied.
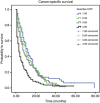
Results: High plasma CRP levels at diagnosis were significantly associated with well-established prognostic factors, including high tumour stage and tumour grade and the administration of chemotherapy (P<0.05). In univariate analysis, we observed that a high plasma CRP level was a consistent factor for poor CSS in PC patients (hazard ratio (HR)=2.21; 95% confidence interval (CI)=1.68-2.92, P<0.001). In multivariate analysis, tumour stage, grade, administration of chemotherapy, a high neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and the highest quartile of CRP levels (HR=1.60, 95% CI=1.16-2.21; P=0.005) were identified as independent prognostic factors in PC patients.
Conclusion: In conclusion, we confirmed a significant association of elevated CRP levels with poor clinical outcome in PC patients. Our results indicate that the plasma CRP level might represent a useful marker for patient stratification in PC management.
Figures

References
-
- Black S, Kushner I, Samols D. C-reactive Protein. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:48487–48490. - PubMed
-
- Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, Trotti A.2010Exocrine and endocrine pancreas AJCC Cancer Staging Manual7th edn,241–249.Springer: New York
-
- Falconer JS, Fearon KC, Ross JA, Elton R, Wigmore SJ, Garden OJ, Carter DC. Acute-phase protein response and survival duration of patients with pancreatic cancer. Cancer. 1995;75:2077–2082. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

