Highly efficient tumor transduction and antitumor efficacy in experimental human malignant mesothelioma using replicating gibbon ape leukemia virus
- PMID: 24201868
- PMCID: PMC8185610
- DOI: 10.1038/cgt.2013.67
Highly efficient tumor transduction and antitumor efficacy in experimental human malignant mesothelioma using replicating gibbon ape leukemia virus
Abstract
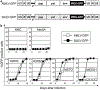
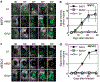
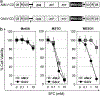
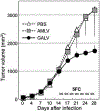
Retroviral replicating vectors (RRVs) have been shown to achieve efficient tumor transduction and enhanced therapeutic benefit in a wide variety of cancer models. Here we evaluated two different RRVs derived from amphotropic murine leukemia virus (AMLV) and gibbon ape leukemia virus (GALV), in human malignant mesothelioma cells. In vitro, both RRVs expressing the green fluorescent protein gene efficiently replicated in most mesothelioma cell lines tested, but not in normal mesothelial cells. Notably, in ACC-MESO-1 mesothelioma cells that were not permissive for AMLV-RRV, the GALV-RRV could spread efficiently in culture and in mice with subcutaneous xenografts by in vivo fluorescence imaging. Next, GALV-RRV expressing the cytosine deaminase prodrug activator gene showed efficient killing of ACC-MESO-1 cells in a prodrug 5-fluorocytosine dose-dependent manner, compared with AMLV-RRV. GALV-RRV-mediated prodrug activator gene therapy achieved significant inhibition of subcutaneous ACC-MESO-1 tumor growth in nude mice. Quantitative reverse transcription PCR demonstrated that ACC-MESO-1 cells express higher PiT-1 (GALV receptor) and lower PiT-2 (AMLV receptor) compared with normal mesothelial cells and other mesothelioma cells, presumably accounting for the distinctive finding that GALV-RRV replicates much more robustly than AMLV-RRV in these cells. These data indicate the potential utility of GALV-RRV-mediated prodrug activator gene therapy in the treatment of mesothelioma.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
CRL and NK are paid consultants to Tocagen Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Ismail-Khan R, Robinson LA, Williams CC Jr, Garrett CR, Bepler G, Simon GR. Malignant pleural mesothelioma: a comprehensive review. Cancer Control 2006; 13: 255–263. - PubMed
-
- van der Most RG, Robinson BW, Nelson DJ. Gene therapy for malignant mesothelioma: beyond the infant years. Cancer Gene Ther 2006; 13: 897–904. - PubMed
-
- Albelda SM, Wiewrodt R, Sterman DH. Gene therapy for lung neoplasms. Clin Chest Med 2002; 23: 265–277. - PubMed
-
- Sterman DH, Recio A, Vachani A, Sun J, Cheung L, DeLong P et al. Long-term follow-up of patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma receiving high-dose adenovirus herpes simplex thymidine kinase/ganciclovir suicide gene therapy. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 7444–7453. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

