Activation of the mitochondrial caspase pathway and subsequent calpain activation in monkey RPE cells cultured under zinc depletion
- PMID: 24202052
- PMCID: PMC3890765
- DOI: 10.1038/eye.2013.239
Activation of the mitochondrial caspase pathway and subsequent calpain activation in monkey RPE cells cultured under zinc depletion
Abstract
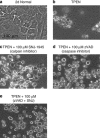
Purpose: Decreased zinc levels in the macula are reported in patients with age-related macular degeneration, and the zinc chelator N,N,N',N'-tetrakis (2- pyridylmethyl) ethylenediamine) (TPEN) causes death of human retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells. The purpose of the present study was to investigate signal transduction pathways during cell death initiated by TPEN, using monkey RPE cells.
Methods: RPE cells were cultured with TPEN. Activation of calpains and caspases, and proteolysis of their substrates were detected by immunoblotting. Incubation of calpain inhibitor SNJ-1945 or caspase inhibitor z-VAD-fmk was used to confirm activation of specific proteases.
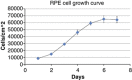
Results: TPEN caused a time-dependent decrease in viable RPE cells. Cell death was accompanied by activation of calpain-1, caspase-9, and caspase-3. SNJ-1945 inhibited calpain activation and slightly inhibited caspase-9 activation. z-VAD-fmk inhibited caspases and calpain-1 activation. TPEN did not activate caspase-12.
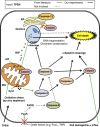
Conclusions: Relative zinc deficiency in RPE cells causes activation of cytosolic calpain and mitochondrial caspase pathways without ER stress.
Figures

References
-
- Strauss O. The retinal pigment epithelium in visual function. Physiol Rev. 2005;85:845–881. - PubMed
-
- Piguet B, Haimovici R, Bird AC. Dominantly inherited drusen represent more than one disorder: a historical review. Eye (Lond) 1995;9 (Pt 1:34–41. - PubMed
-
- Newsome DA, Miceli MV, Tate DJ, Jr, Alcock NW, Oliver PD. Zinc content of human retinal pigment epithelium decreases with age and macular degeneration, but superoxide dismutase activity increases. J Trace Elem Exp Med. 1995;8:193–199.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

