Characterization of a Dual CDC7/CDK9 Inhibitor in Multiple Myeloma Cellular Models
- PMID: 24202326
- PMCID: PMC3795371
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers5030901
Characterization of a Dual CDC7/CDK9 Inhibitor in Multiple Myeloma Cellular Models
Abstract
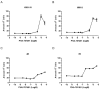
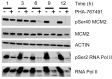
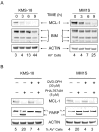
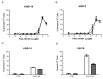
Two key features of myeloma cells are the deregulation of the cell cycle and the dependency on the expression of the BCL2 family of anti-apoptotic proteins. The cell division cycle 7 (CDC7) is an essential S-phase kinase and emerging CDC7 inhibitors are effective in a variety of preclinical cancer models. These compounds also inhibit CDK9 which is relevant for MCL-1 expression. The activity and mechanism of action of the dual CDC7/CDK9 inhibitor PHA-767491 was assessed in a panel of multiple myeloma cell lines, in primary samples from patients, in the presence of stromal cells and in combination with drugs used in current chemotherapeutic regimens. We report that in all conditions myeloma cells undergo cell death upon PHA-767491 treatment and we report an overall additive effect with melphalan, bortezomib and doxorubicin, thus supporting further assessment of targeting CDC7 and CDK9 in multiple myeloma.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of action of a dual Cdc7/Cdk9 kinase inhibitor against quiescent and proliferating CLL cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2011 Sep;10(9):1624-34. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-1119. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011. PMID: 21768328
-
Dual Inhibition of Cdc7 and Cdk9 by PHA-767491 Suppresses Hepatocarcinoma Synergistically with 5-Fluorouracil.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2015;15(3):196-204. doi: 10.2174/1568009615666150212112753. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2015. PMID: 25643258
-
Positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb) is a therapeutic target in human multiple myeloma.Oncotarget. 2017 Aug 1;8(35):59476-59491. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19761. eCollection 2017 Aug 29. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28938651 Free PMC article.
-
Current and emerging therapies for patients with acute myeloid leukemia: a focus on MCL-1 and the CDK9 pathway.Am J Manag Care. 2018 Aug;24(16 Suppl):S356-S365. Am J Manag Care. 2018. PMID: 30132679 Review.
-
Bortezomib: a review of its use in patients with multiple myeloma.Drugs. 2009;69(7):859-88. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200969070-00006. Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19441872 Review.
Cited by
-
Kinase inhibitors as potential agents in the treatment of multiple myeloma.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 6;7(49):81926-81968. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10745. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27655636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DBF4, not DRF1, is the crucial regulator of CDC7 kinase at replication forks.J Cell Biol. 2024 Aug 5;223(8):e202402144. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202402144. Epub 2024 Jun 12. J Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38865090 Free PMC article.
-
The Covalent CDK7 Inhibitor THZ1 Potently Induces Apoptosis in Multiple Myeloma Cells In Vitro and In Vivo.Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Oct 15;25(20):6195-6205. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-3788. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31358538 Free PMC article.
-
CDK9 inhibitors for the treatment of solid tumors.Biochem Pharmacol. 2024 Nov;229:116470. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116470. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Biochem Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39127153 Review.
-
P-TEFb as A Promising Therapeutic Target.Molecules. 2020 Feb 14;25(4):838. doi: 10.3390/molecules25040838. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32075058 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Altekruse S.F., Kosary C.L., Krapcho M., Neyman N., Aminou R., Waldron W., Ruhl J., Howlader N., Tatlovich Z., Cho H., Mariotto A., et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2007. National Cancer Institute; Bethesda, MD, USA: 2009.
-
- Ely S., di Liberto M., Niesvizky R., Baughn L.B., Cho H.J., Hatada E.N., Knowles D.M., Lane J., Chen-Kiang S. Mutually exclusive cyclin-dependent kinase 4/cyclin D1 and cyclin-dependent kinase 6/cyclin D2 pairing inactivates retinoblastoma protein and promotes cell cycle dysregulation in multiple myeloma. Cancer Res. 2005;65:11345–11353. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2159. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shaughnessy J.D., Jr., Zhan F., Burington B.E., Huang Y., Colla S., Hanamura I., Stewart J.P., Kordsmeier B., Randolph C., Williams D.R., et al. A validated gene expression model of high-risk multiple myeloma is defined by deregulated expression of genes mapping to chromosome 1. Blood. 2007;109:2276–2284. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-07-038430. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

