Short-term estradiol supplementation potentiates low-dose ghrelin action in the presence of GHRH or somatostatin in older women
- PMID: 24203062
- PMCID: PMC3879681
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2013-3043
Short-term estradiol supplementation potentiates low-dose ghrelin action in the presence of GHRH or somatostatin in older women
Abstract
Context: Ghrelin is a potent gastric-derived GH-releasing peptide. How ghrelin interacts with sex steroids, GHRH, and somatostatin (SS) is not known.
Objective: Our objective was to test the hypotheses that ghrelin's interactions with GHRH (synergistic) and SS (disinhibitory) are ghrelin dose-dependent and amplified by estrogen. SUBJECTS, SETTING, AND DESIGN: Healthy postmenopausal women were treated with placebo (n=12) or 17β-estradiol (E2) (n=12) at the Center for Translational Science Activities in a randomized double-blind prospective study.
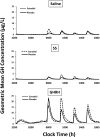
Methods: Ghrelin dose-dependence was assessed by nonlinear curve fitting of the relationship between deconvolved GH secretory-burst mass and 5 randomly ordered ghrelin doses (0, 0.03, 0.135, 0.6, and 2.7 μg/kg bolus iv) during saline, GHRH, and SS infusion.
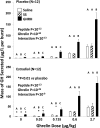
Results: Under placebo, neither GHRH nor SS altered the ED50 of ghrelin (range 0.64-0.67 μg/kg). Under E2 (median E2 88 pg/mL), the ED50 of ghrelin declined in the presence of GHRH to 0.52 μg/kg. In contrast, the efficacy of ghrelin rose markedly during GHRH vs saline exposure with and without E2: placebo and saline 52±1.0 vs GHRH 173±3.8 μg/L; and E2 and saline 56±0.90 vs GHRH 174±3.7 μg/L. Sensitivity to ghrelin was similar under all conditions.
Summary: Short-term E2 supplementation in postmenopausal women reduces the ED50 (increases the potency) of ghrelin when GHRH is present, without altering ghrelin efficacy (maximal effect) or hypothalamo-pituitary sensitivity (slope of dose response) to ghrelin. The data suggest possible physiological interactions among sex steroids (endogenous), ghrelin, and GHRH during E2 replacement in postmenopausal women.
Figures


References
-
- Giustina A, Veldhuis JD. Pathophysiology of the neuroregulation of growth hormone secretion in experimental animals and the human. Endocr Rev. 1998;19(6):717–797 - PubMed
-
- Veldhuis JD, Roemmich JN, Richmond EJ, Bowers CY. Somatotropic and gonadotropic axes linkages in infancy, childhood, and the puberty-adult transition. Endocr Rev. 2006;27(2):101–140 - PubMed
-
- Farhy LS, Bowers CY, Veldhuis JD. Model-projected mechanistic bases for sex differences in growth hormone regulation in humans. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007;292(4):R1577–R1593 - PubMed
-
- Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, Nakazato M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature. 1999;402:656–660 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

