Age effects on mouse and human B cells
- PMID: 24203437
- PMCID: PMC5673119
- DOI: 10.1007/s12026-013-8440-9
Age effects on mouse and human B cells
Abstract
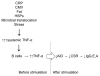
Our laboratory has contributed to the areas of B cell receptor (BCR) and pre-BCR gene identification and transcription and has focused on the problem of the aged immune system in mice and humans for the last 15 years. We have found biomarkers for the decrease in B cell function in aged mice and humans. These include decreases in immunoglobulin (Ig) class switch (e.g., IgM to IgG), decreases in the enzyme AID (activation-induced cytidine deaminase) and decreases in the transcription factor E47. The E47 mRNA stability is decreased in old B cells due to decreased phospho-MAPKinase and phospho-TTP (tristetraprolin). Inflammation, e.g., TNF-α, which increases with age, impacts B cells directly by increasing their TNF-α and NF-κB and leads to the above decreased pathway. Both class switch and affinity maturation are decreased in elderly responses to the influenza vaccine and biomarkers we have found (numbers and percentages of switched memory B cells and AID in stimulated B cells in culture) can predict a beneficial or decreased immune response to the vaccine. Current and future avenues to improve the humoral immune response in the elderly are discussed.
Figures
References
-
- Hodes RJ. Aging and the immune system. Immunol Rev. 1997;160:5–8. - PubMed
-
- LeMaoult J, Szabo P, Weksler ME. Effect of age on humoral immunity, selection of the B-cell repertoire and B-cell development. Immunol Rev. 1997;160:115–26. - PubMed
-
- Pawelec G, Barnett Y, Forsey R, Frasca D, Globerson A, McLeod J, et al. T cells and aging, January 2002 update. Front Biosci J virtual Library. 2002;7:d1056–183. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

