Mutations in PCBD1 cause hypomagnesemia and renal magnesium wasting
- PMID: 24204001
- PMCID: PMC3935582
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2013040337
Mutations in PCBD1 cause hypomagnesemia and renal magnesium wasting
Abstract
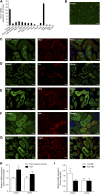
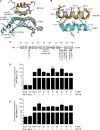
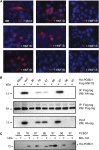
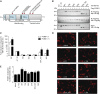
Mutations in PCBD1 are causative for transient neonatal hyperphenylalaninemia and primapterinuria (HPABH4D). Until now, HPABH4D has been regarded as a transient and benign neonatal syndrome without complications in adulthood. In our study of three adult patients with homozygous mutations in the PCBD1 gene, two patients were diagnosed with hypomagnesemia and renal Mg(2+) loss, and two patients developed diabetes with characteristics of maturity onset diabetes of the young (MODY), regardless of serum Mg(2+) levels. Our results suggest that these clinical findings are related to the function of PCBD1 as a dimerization cofactor for the transcription factor HNF1B. Mutations in the HNF1B gene have been shown to cause renal malformations, hypomagnesemia, and MODY. Gene expression studies combined with immunohistochemical analysis in the kidney showed that Pcbd1 is expressed in the distal convoluted tubule (DCT), where Pcbd1 transcript levels are upregulated by a low Mg(2+)-containing diet. Overexpression in a human kidney cell line showed that wild-type PCBD1 binds HNF1B to costimulate the FXYD2 promoter, the activity of which is instrumental in Mg(2+) reabsorption in the DCT. Of seven PCBD1 mutations previously reported in HPABH4D patients, five mutations caused proteolytic instability, leading to reduced FXYD2 promoter activity. Furthermore, cytosolic localization of PCBD1 increased when coexpressed with HNF1B mutants. Overall, our findings establish PCBD1 as a coactivator of the HNF1B-mediated transcription necessary for fine tuning FXYD2 transcription in the DCT and suggest that patients with HPABH4D should be monitored for previously unrecognized late complications, such as hypomagnesemia and MODY diabetes.
Figures
References
-
- Adalat S, Woolf AS, Johnstone KA, Wirsing A, Harries LW, Long DA, Hennekam RC, Ledermann SE, Rees L, van’t Hoff W, Marks SD, Trompeter RS, Tullus K, Winyard PJ, Cansick J, Mushtaq I, Dhillon HK, Bingham C, Edghill EL, Shroff R, Stanescu H, Ryffel GU, Ellard S, Bockenhauer D: HNF1B mutations associate with hypomagnesemia and renal magnesium wasting. J Am Soc Nephrol 20: 1123–1131, 2009 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Faguer S, Decramer S, Chassaing N, Bellanné-Chantelot C, Calvas P, Beaufils S, Bessenay L, Lengelé JP, Dahan K, Ronco P, Devuyst O, Chauveau D: Diagnosis, management, and prognosis of HNF1B nephropathy in adulthood. Kidney Int 80: 768–776, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Glaudemans B, Knoers NV, Hoenderop JG, Bindels RJ: New molecular players facilitating Mg(2+) reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule. Kidney Int 77: 17–22, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Meij IC, Koenderink JB, van Bokhoven H, Assink KF, Groenestege WT, de Pont JJ, Bindels RJ, Monnens LA, van den Heuvel LP, Knoers NV: Dominant isolated renal magnesium loss is caused by misrouting of the Na(+),K(+)-ATPase gamma-subunit. Nat Genet 26: 265–266, 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

