A laminar flow unit for the care of critically ill newborn infants
- PMID: 24204178
- PMCID: PMC3804569
- DOI: 10.2147/MDER.S51270
A laminar flow unit for the care of critically ill newborn infants
Abstract
Introduction: Medical and nursing care of newborns is predicated on the delicate control and balance of several vital parameters. Closed incubators and open radiant warmers are the most widely used devices for the care of neonates in intensive care; however, several well-known limitations of these devises have not been resolved. The use of laminar flow is widely used in many fields of medicine, and may have applications in neonatal care.
Objective: To describe the neonatal laminar flow unit, a new equipment we designed for care of ill newborns.
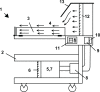
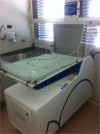
Methods: The idea, design, and development of this device was completed in Sao Paulo, Brazil. The unit is an open mobile bed designed with the objective of maintaining the advantages of the incubator and radiant warmer, while overcoming some of their inherent shortcomings; these shortcomings include noise, magnetic fields and acrylic barriers in incubators, and lack of isolation and water loss through skin in radiant warmers. The unit has a pump that aspirates environmental air which is warmed by electrical resistance and decontaminated with High Efficiency Particulate Air Filter (HEPA) filters (laminar flow). The flow is directed by an air flow directioner. The unit has an embedded humidifier to increase humidity in the infant's microenvironment and a servo control mechanism for regulation of skin temperature.
Results: The laminar flow unit is open and facilitates access of care providers and family, which is not the case in incubators. It provides warming by convection at an air velocity of 0.45 m/s, much faster than an incubator (0.1 m/s). The system provides isolation 1000 class (less than 1,000 particles higher than 0.3 micron per cubic feet at all times). This is much more protection than an incubator provides and more than radiant warmers, which have no isolation whatsoever. Additionally, it provides humidification of the newborn's microenvironment (about 60% relative humidity), which is impossible with a radiant warmer, which produces high water body loss. It has no mechanical barriers like acrylic walls, its magnetic field is lower than an incubator (0.25 μt versus 1.2 μt), and the noise is minimal compared to incubators. The unit is also able to provide controlled total body hypothermia, which is not possible with either of the other two units.
Conclusion: The laminar flow unit for neonatal care is a novel device which we recently developed. The introduction of laminar flow technology represents a real innovation in the neonatal field. We have described the various components of the unit and the potential advantages for management of ill neonates. This will hopefully lead to improved clinical outcomes and more effective neonatal management and safety.
Keywords: incubator; laminar flow; newborn intensive care; radiant warmer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Infant incubators and radiant warmers.Early Hum Dev. 1983 Oct;8(3-4):351-75. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(83)90018-x. Early Hum Dev. 1983. PMID: 6641579
-
Neonatal warming devices: What can be recommended for low-resource settings when skin-to-skin care is not feasible?Front Pediatr. 2023 Apr 25;11:1171258. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1171258. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37181431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A clinical comparison of radiant warmer and incubator care for preterm infants from birth to 1800 grams.Pediatrics. 2001 Aug;108(2):395-401. doi: 10.1542/peds.108.2.395. Pediatrics. 2001. PMID: 11483805 Clinical Trial.
-
The heat balance of small babies nursed in incubators and under radiant warmers.Early Hum Dev. 1982 Apr;6(2):131-43. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(82)90100-1. Early Hum Dev. 1982. PMID: 7094851
-
Radiant energy and insensible water loss in the premature newborn infant nursed under a radiant warmer.Clin Perinatol. 1982 Oct;9(3):483-503. Clin Perinatol. 1982. PMID: 6761034 Review.
References
-
- Baker JP. The incubator and the medical discovery of the premature infant. J Perinatol. 2000;20(5):321–328. - PubMed
-
- Gray PH, Flenady V. Cot-nursing versus incubator care for preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;(8):CD003062. - PubMed
-
- McIntosh N, Lyon AJ. Keeping infants warm. Pediatrics. 2002;110(2 Pt 1):424–425. - PubMed
-
- Apedoh A, el Hajajji A, Telliez F, Bouferrache B, Libert JP, Rachid A. Mannequin-assessed dry-heat exchanges in the incubator-nursed newborn. Biomed Instrum Technol. 1999 Sep-Oct;33(5):446–54. - PubMed
-
- Johnson AN. Neonatal response to control of noise inside the incubator. Pediatr Nurs. 2001;27(6):600–605. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

