Survival of the replication checkpoint deficient cells requires MUS81-RAD52 function
- PMID: 24204313
- PMCID: PMC3814295
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003910
Survival of the replication checkpoint deficient cells requires MUS81-RAD52 function
Abstract
In checkpoint-deficient cells, DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) are produced during replication by the structure-specific endonuclease MUS81. The mechanism underlying MUS81-dependent cleavage, and the effect on chromosome integrity and viability of checkpoint deficient cells is only partly understood, especially in human cells. Here, we show that MUS81-induced DSBs are specifically triggered by CHK1 inhibition in a manner that is unrelated to the loss of RAD51, and does not involve formation of a RAD51 substrate. Indeed, CHK1 deficiency results in the formation of a RAD52-dependent structure that is cleaved by MUS81. Moreover, in CHK1-deficient cells depletion of RAD52, but not of MUS81, rescues chromosome instability observed after replication fork stalling. However, when RAD52 is down-regulated, recovery from replication stress requires MUS81, and loss of both these proteins results in massive cell death that can be suppressed by RAD51 depletion. Our findings reveal a novel RAD52/MUS81-dependent mechanism that promotes cell viability and genome integrity in checkpoint-deficient cells, and disclose the involvement of MUS81 to multiple processes after replication stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
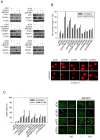
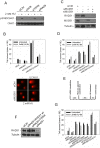

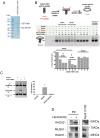

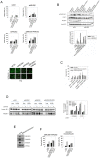


References
-
- Branzei D, Foiani M (2009) The checkpoint response to replication stress. DNA Repair 8: 1038–1046. - PubMed
-
- Friedel AM, Pike BL, Gasser SM (2009) ATR/Mec1: coordinating fork stability and repair. Current Opinion in Cell Biology 21: 237–244. - PubMed
-
- Cotta-Ramusino C, Fachinetti D, Lucca C, Doksani Y, Lopes M, et al. (2005) Exo1 processes stalled replication forks and counteracts fork reversal in checkpoint-defective cells. Molecular Cell 17: 153–159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

