Predictors of CD4:CD8 ratio normalization and its effect on health outcomes in the era of combination antiretroviral therapy
- PMID: 24204912
- PMCID: PMC3813720
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077665
Predictors of CD4:CD8 ratio normalization and its effect on health outcomes in the era of combination antiretroviral therapy
Abstract
Background: HIV leads to CD4:CD8 ratio inversion as immune dysregulation progresses. We examined the predictors of CD4:CD8 normalization after combination antiretroviral therapy (cART) and determined whether normalization is associated with reduced progression to AIDS-defining illnesses (ADI) and death.
Methods: A Canadian cohort of HIV-positive adults with CD4:CD8<1.2 prior to starting cART from 2000-2010 were analyzed. Predictors of (1) reaching a CD4:CD8 ≥ 1.2 on two separate follow-up visits >30 days apart, and (2) ADI and death from all causes were assessed using adjusted proportional hazards models.
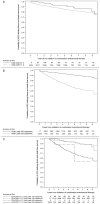
Results: 4206 patients were studied for a median of 2.77 years and 306 (7.2%) normalized their CD4:CD8 ratio. Factors associated with achieving a normal CD4:CD8 ratio were: baseline CD4+ T-cells >350 cells/mm(3), baseline CD8+ T-cells <500 cells/mm(3), time-updated HIV RNA suppression, and not reporting sex with other men as a risk factor. There were 213 ADIs and 214 deaths in 13476 person-years of follow-up. Achieving a normal CD4:CD8 ratio was not associated with time to ADI/death.
Conclusions: In our study, few individuals normalized their CD4:CD8 ratios within the first few years of initiating modern cART. This large study showed no additional short-term predictive value of the CD4:CD8 ratio for clinical outcomes after accounting for other risk factors including age and HIV RNA.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Fahey JL, Giorgi J, Martinez-Maza O, Detels R, Mitsuyasu R, et al. (1987) Immune pathogenesis of AIDS and related syndromes. Ann Inst Pasteur Immunol 138: 245–252. - PubMed
-
- Bouscarat F, Levacher M, Landman R, Muffat-Joly M, Girard PM, et al. (1998) Changes in blood CD8+ lymphocyte activation status and plasma HIV RNA levels during antiretroviral therapy. AIDS 12: 1267–1273. - PubMed
-
- Taylor JM, Fahey JL, Detels R, Giorgi JV (1989) CD4 percentage, CD4 number, and CD4:CD8 ratio in HIV infection: which to choose and how to use. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2: 114–124. - PubMed
-
- Fahey JL, Taylor JM, Detels R, Hofmann B, Melmed R, et al. (1990) The prognostic value of cellular and serologic markers in infection with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. N Engl J Med 322: 166–172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

